Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
उत्तर
Mean velocity is given by \[V_{avg} = \sqrt{\frac{8RT}{\pi M}}\]
Let temperature for H and He respectively be T1 and T2, respectively.
For hydrogen:
MH = 2g = 2 \[\times\] 10-3 kg
For helium:
MHe= 4 g = 4 \[\times\] 10-3 kg
Now,
A/q \[\sqrt{\frac{8R T_1}{\pi M_H}} = \sqrt{\frac{8R T_2}{\pi M_{He}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt{\frac{8R T_1}{2 \times {10}^{- 3} \pi}} = \sqrt{\frac{8R T_2}{\pi \times 4 \times {10}^{- 3}}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \sqrt{\frac{T_1}{2}} = \sqrt{\frac{T_2}{4}}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{T_1}{T_2} = \frac{1}{2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow T_1 : T_2 = 1: 2\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
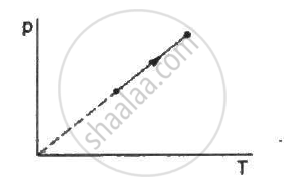
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
Find the number of molecules of an ideal gas in a volume of 1.000 cm3 at STP.
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
0.040 g of He is kept in a closed container initially at 100.0°C. The container is now heated. Neglecting the expansion of the container, calculate the temperature at which the internal energy is increased by 12 J.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
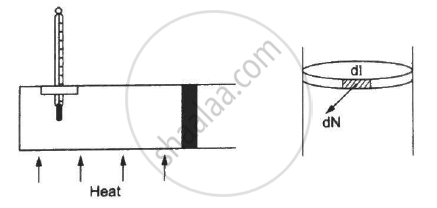
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
Compare the rates of emission of heat by a blackbody maintained at 727°C and at 227°C, if the black bodies are surrounded by an enclosure (black) at 27°C. What would be the ratio of their rates of loss of heat?
The number of degrees of freedom, for the vibrational motion of a polyatomic molecule, depends on the ______
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
