Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
उत्तर
Here,
Temperature in Simla, T1= 15 + 273 = 288 K
Pressure in Simla, P1 = 0.72 m of Hg
Temperature in Kalka, T2= 35+273 = 308 K
Pressure in Kalka, P2 = 0.76 m of Hg
Let density of air at Simla and Kalka be ρ1 and ρ2 respectively. Then,
\[PV = \frac{m}{M}RT\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{m}{V} = \frac{PM}{RT}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \rho = \frac{PM}{RT}\]
Thus, \[\rho_1 = \frac{P_1 M}{R T_1}\]
\[\rho_2 = \frac{P_2 M}{R T_2}\]
Taking ratios , we get
\[\frac{\rho_1}{\rho_2} = \frac{P_1}{T_1} \times \frac{T_2}{P_2}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\rho_1}{\rho_2} = \frac{0 . 72}{288} \times \frac{308}{0 . 76}\]
\[ \Rightarrow \frac{\rho_2}{\rho_1} = 0 . 987\]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law pV2 = constant. The gas is initially at a temperature T and volume V. Find the temperature when it expands to a volume 2V.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
Answer in brief:
What will happen to the mean square speed of the molecules of a gas if the temperature of the gas increases?
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
Compare the rates of emission of heat by a blackbody maintained at 727°C and at 227°C, if the black bodies are surrounded by an enclosure (black) at 27°C. What would be the ratio of their rates of loss of heat?
Find the temperature of a blackbody if its spectrum has a peak at (a) λmax = 700 nm (visible), (b) λmax = 3 cm (microwave region) (c) λmax = 3 m (short radio waves). (Take Wien’s constant b = 2.897 × 10-3 m.K).
A metal cube of length 4 cm radiates heat at the rate of 10 J/s. Find its emissive power at a given temperature.
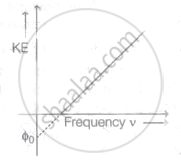
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
A ring of mass m and radius r rotates about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity `omega`. Its kinetic energy is ______.
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, KP are related as ______.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
Show that the average energy per molecule is proportional to the absolute temperature T of the gas.
