Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Show that the average energy per molecule is proportional to the absolute temperature T of the gas.
उत्तर
The expression for the pressure exerted by a gas on the basis of kinetic theory of gas is given by
`P = 1/3(Nm)/v v_(rms)^2`
`PV=1/3xx2xx1/2xxNmv_(rms)^2`
`PV = 2/3E, ...(becauseE=1/2xxNmv_(rms)^2)`
By definition,
PV = RT ...(for one mole)
`RT = 2/3E`
`E=3/2RT`
`E=3/2Nk_BT ...(becauseR=Nk_B)`
`E/N=3/2k_BT`
`E/NmuT`
Average energy, per molecule, is directly proportional to absolute temperature T of the gas.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
A gas is kept in an enclosure. The pressure of the gas is reduced by pumping out some gas. Will the temperature of the gas decrease by Charles's low?
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
A gas cylinder has walls that can bear a maximum pressure of 1.0 × 106 Pa. It contains a gas at 8.0 × 105 Pa and 300 K. The cylinder is steadily heated. Neglecting any change in the volume, calculate the temperature at which the cylinder will break.
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area A fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is T0 and its pressure is p0 which equals the atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the tension in the wire? (b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to 2T0 ?

A glass contains some water at room temperature 20°C. Refrigerated water is added to it slowly. when the temperature of the glass reaches 10°C, small droplets condense on the outer surface. Calculate the relative humidity in the room. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 17.5 mm of mercury is 20°C and at 8.9 mm of mercury it is 10°C.
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
The average translational kinetic energy of gas molecules depends on ____________.
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
When photons of energy hv fall on a metal plate of work function 'W0', photoelectrons of maximum kinetic energy 'K' are ejected. If the frequency of the radiation is doubled, the maximum kinetic energy of the ejected photoelectrons will be ______.
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
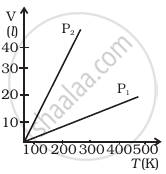
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity vo. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
Assuming the expression for the pressure P exerted by an ideal gas, prove that the kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas is `3/2` P.
If a = 0. 72 and t = 0.04, then the value of r is ______.
