Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
उत्तर
Consider the diagram
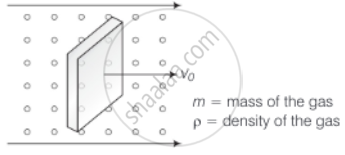
Let n = number of molecules per unit volume
Vrms = rms speed of the gas molecules
When a block is moving with speed v0, relative speed of molecules w.r.t. front face = v + v0
Coming head-on, momentum transferred to block per collision = 2m (v + v0), where, m = mass of the molecule.
The number of collisions in time Δt = m(v + v0)2nAΔt, where, A = area of cross-section of block and factor of 1/2 appears due to particles moving towards the block.
∴ The momentum transferred in time Δt = m(v + v0)2nAΔt from the front surface.
Similarly, momentum transferred in time Δt = m(v – v0)2nAΔt ......(From the back surface)
∴ Net force (drag force) = mnA[(v + v0)2 – (v – v0)2] .....[From front]
= mnA (4vv0)
= (4 mnAv)v0
= (4ρAv)v0 ......(i)
Where we have assumed ρ = `(mn)/V = M/V`
If v = velocity along the x-axis
Then, we can write KE = `1/2 mv^2 = 1/2 K_BT`
⇒ `v = sqrt((K_BT)/m)` .....`[(K_B = "Boltzmann constant"),(KE = "Kinetic energy"),(T = "Temperature")]`
∴ From equation (i), Drag force = (4ρAv)v0 = `4ρA sqrt((K_BT)/m) v_0`.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
The temperature and the dew point in an open room are 20°C and 10°C. If the room temperature drops to 15°C, what will be the new dew point?
An adiabatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm2 is closed at one end and fitted with a piston at the other end. The tube contains 0.03 g of an ideal gas. At 1 atm pressure and at the temperature of the surrounding, the length of the gas column is 40 cm. The piston is suddenly pulled out to double the length of the column. The pressure of the gas falls to 0.355 atm. Find the speed of sound in the gas at atmospheric temperature.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
Energy is emitted from a hole in an electric furnace at the rate of 20 W when the temperature of the furnace is 727°C. What is the area of the hole? (Take Stefan’s constant σ to be 5.7 × 10-8 Js-1 m-2K-4.)
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
23Ne decays to 23Na by negative beta emission. Mass of 23Ne is 22.994465 amu mass of 23Na is 22.989768 amu. The maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons neglecting the kinetic energy of recoiling product nucleus is ______ MeV.
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, KP are related as ______.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
