Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Energy is emitted from a hole in an electric furnace at the rate of 20 W when the temperature of the furnace is 727°C. What is the area of the hole? (Take Stefan’s constant σ to be 5.7 × 10-8 Js-1 m-2K-4.)
उत्तर
`"Q"/"t" = 20`W, T = 273 + 727 = 1000 K
σ = 5.7 × 10-8 Js-1 m-2K-4.
`"Q"/"t" = sigma"AT"^4`
∴ The area of the hole,
A = `("Q"//"t")/(sigma"T"^4) = 20/((5.7 xx 10^-8)(10^3)^4)` m2
`= (20xx10^-4)/5.7 = 3.509 xx 10^-4` m2
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
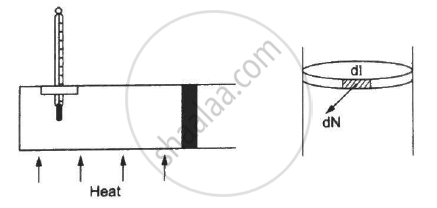
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
The temperature and the dew point in an open room are 20°C and 10°C. If the room temperature drops to 15°C, what will be the new dew point?
A glass contains some water at room temperature 20°C. Refrigerated water is added to it slowly. when the temperature of the glass reaches 10°C, small droplets condense on the outer surface. Calculate the relative humidity in the room. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 17.5 mm of mercury is 20°C and at 8.9 mm of mercury it is 10°C.
An adiabatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm2 is closed at one end and fitted with a piston at the other end. The tube contains 0.03 g of an ideal gas. At 1 atm pressure and at the temperature of the surrounding, the length of the gas column is 40 cm. The piston is suddenly pulled out to double the length of the column. The pressure of the gas falls to 0.355 atm. Find the speed of sound in the gas at atmospheric temperature.
Answer in brief:
What will happen to the mean square speed of the molecules of a gas if the temperature of the gas increases?
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
Above what temperature, all bodies radiate electromagnetic radiation?
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
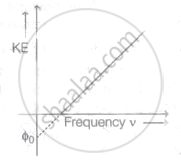
The graph of kinetic energy against the frequency v of incident light is as shown in the figure. The slope of the graph and intercept on X-axis respectively are ______.
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
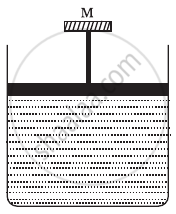
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
23Ne decays to 23Na by negative beta emission. Mass of 23Ne is 22.994465 amu mass of 23Na is 22.989768 amu. The maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons neglecting the kinetic energy of recoiling product nucleus is ______ MeV.
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, KP are related as ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
