Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
उत्तर
m2 = m1/3, vrms2 = 2vrms1 as the speeds of all molecules are doubled
Pressure, P = `1/3."mN"/"V"."v"^2`rms
∴ `"P"_1 = 1/3,("m"_1"N")/"V"."v"_"rms 1"^2` and
∴ `"P"_2 = 1/3,("m"_2"N")/"V"."v"_"rms 2"^2`
∴ `"P"_2/"P"_1 = ("m"_2/"m"_1)(("v"_"rms2"^2)/("v"_"rms 1"^2))`
`=("m"_2/"m"_1)(("v"_"rms 2")/("v"_"rms 1"))^2`
`= (("m"_1//3)/"m"_1)(2)^2 = 4/3`
∴ `"P"_2 = 4/3"P"_1 = 4/3"P"`
This is the resultant pressure.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
Find the number of molecules of an ideal gas in a volume of 1.000 cm3 at STP.
A gas cylinder has walls that can bear a maximum pressure of 1.0 × 106 Pa. It contains a gas at 8.0 × 105 Pa and 300 K. The cylinder is steadily heated. Neglecting any change in the volume, calculate the temperature at which the cylinder will break.
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
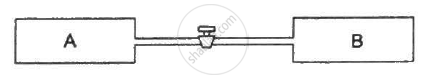
Figure shows two vessels A and B with rigid walls containing ideal gases. The pressure, temperature and the volume are pA, TA, V in the vessel A and pB, TB, V in the vessel B. The vessels are now connected through a small tube. Show that the pressure p and the temperature T satisfy `Ρ/T = 1/2 ({P_A}/{T_A}+{P_B}/{T_B))` when equilibrium is achieved.
An ideal gas is trapped between a mercury column and the closed-end of a narrow vertical tube of uniform base containing the column. The upper end of the tube is open to the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure equals 76 cm of mercury. The lengths of the mercury column and the trapped air column are 20 cm and 43 cm respectively. What will be the length of the air column when the tube is tilted slowly in a vertical plane through an angle of 60°? Assume the temperature to remain constant.
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
The temperature and the dew point in an open room are 20°C and 10°C. If the room temperature drops to 15°C, what will be the new dew point?
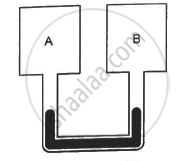
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
Under which condition laws of Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac are valid?
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
A metal cube of length 4 cm radiates heat at the rate of 10 J/s. Find its emissive power at a given temperature.
The average translational kinetic energy of gas molecules depends on ____________.
Assuming the expression for the pressure exerted by the gas on the wall of the container, it can be shown that pressure is ______.
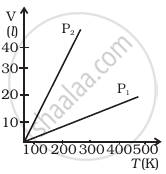
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
23Ne decays to 23Na by negative beta emission. Mass of 23Ne is 22.994465 amu mass of 23Na is 22.989768 amu. The maximum kinetic energy of emitted electrons neglecting the kinetic energy of recoiling product nucleus is ______ MeV.
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
