Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
उत्तर
Data: VA = 2VB, TA = 2TB, PA = 2PB
PV = nRT
or PV = NkBT
Find: `"N"_"A"/"N"_"B"` = ?
∴ The number of molecules, N = `"PV"/("k"_"B""T")`
∴ NA = `("P"_"A""V"_"A")/("k"_"B""T"_"A")` and NB = `("P"_"B""V"_"B")/("k"_"B""T"_"B")`
∴ `"N"_"A"/"N"_"B" = ("P"_"A"/"P"_"B")("V"_"A"/"V"_"B")("T"_"B"/"T"_"A")`
∴ `"N"_"A"/"N"_"B" = ((2"P"_"B")/"P"_"B")((2"V"_"B")/"V"_"B")("T"_"B"/(2"T"_"B"))`
∴ `"N"_"A"/"N"_"B" = cancel(2) xx 2 xx 1/cancel(2)`
∴ `"N"_"A"/"N"_"B" = 2/1`
∴ `"N"_"A"/"N"_"B"` = 2 : 1
This is the required ratio.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
If the molecules were not allowed to collide among themselves, would you expect more evaporation or less evaporation?
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
The average translational kinetic energy of air molecules is 0.040 eV (1 eV = 1.6 × 10−19J). Calculate the temperature of the air. Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1.
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law pV2 = constant. The gas is initially at a temperature T and volume V. Find the temperature when it expands to a volume 2V.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
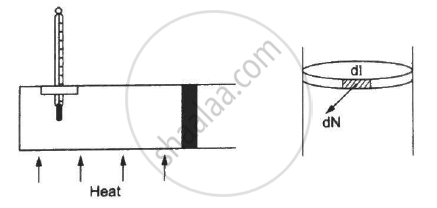
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Find the temperature of a blackbody if its spectrum has a peak at (a) λmax = 700 nm (visible), (b) λmax = 3 cm (microwave region) (c) λmax = 3 m (short radio waves). (Take Wien’s constant b = 2.897 × 10-3 m.K).
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
Under which condition laws of Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac are valid?
On what, the values of absorption coefficient, reflection coefficient, and transmission coefficient depend, in addition to the material of the object on which the radiation is an incident?
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
Assuming the expression for the pressure exerted by the gas on the wall of the container, it can be shown that pressure is ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
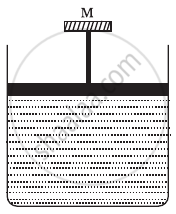
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
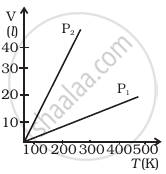
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
Explain why there is no atmosphere on moon.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
2000 calories of radiant heat is incident on a body. If the body absorbs 550 calories of heat, find the coefficient of emmission of the body.
