Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
उत्तर
Yes, it is possible to boil water at 300C by reducing the external pressure. A liquid boils when its vapour pressure equals external pressure. By lowering the external pressure, it is possible to boil the liquid at low temperatures.
No, the flask containing water boiling at 300C will not be hot.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
The pressure of an ideal gas is written as \[P = \frac{2E}{3V}\] . Here E refers to
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
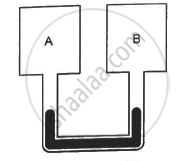
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
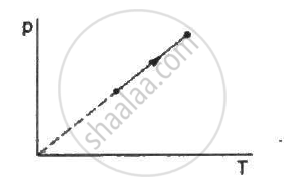
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Calculate the ratio of the mean square speeds of molecules of a gas at 30 K and 120 K.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
On what, the values of absorption coefficient, reflection coefficient, and transmission coefficient depend, in addition to the material of the object on which the radiation is an incident?
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
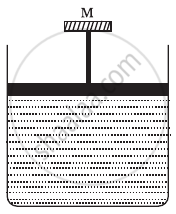
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
Show that the average energy per molecule is proportional to the absolute temperature T of the gas.
