Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
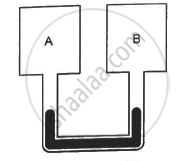
उत्तर
Given:
Volume of gas in each vessel, V = 200 cm3
Specific heat at constant volume of the gas, Cv = 12.5 J/mol-K
Initial temperature of the gas, T = 300 K
Initial pressure of the gas, P = 75 cm of Hg
(a) Using the ideal gas equation, number of moles of gases in each vessel,
75 cm of Hg = 99991.5 N/m2
`"n" = ("P""V")/("R""T")`
`= (99991.5 xx 200 xx 10^-6)/(8.3 xx 300)`
= 8031.4 xx 10-6
=0.008
(b) Heat is supplied to the gas, but dV is zero as the container has rigid walls.
So, dW = P Δ V = 0
From first law of thermodynamics,
dQ = dU
⇒ 5 = nCvdT
⇒ 5 = 0.008 × 12.5 × dT
⇒ dT = 50 for A
`"P"/"T" = "P"_"A"/"T"_"A" ` because volume is kept constant.
Q = nCvdT
`"T" = "Q"/("n""C"_"v")`
`75/300 =( "P"_"A" xx 0.008 xx 12.5)/5`
`"P"_"A" = (75 xx 5)/(300 xx 0.008 xx 12.5)`
= 12.5 cm of Hg
Again ,` "P"/"T" = "P"_"B"/"T"_"B" [ For container B]`
`75/300 =( "P"_"B" xx 0.008 xx 12.5 )/10`
PB = 25 cm of Hg
The distance moved by the mercury,
PB − PA = 25 − 12.5 = 12.5 cm
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
A gas cylinder has walls that can bear a maximum pressure of 1.0 × 106 Pa. It contains a gas at 8.0 × 105 Pa and 300 K. The cylinder is steadily heated. Neglecting any change in the volume, calculate the temperature at which the cylinder will break.
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
Answer in brief:
What will happen to the mean square speed of the molecules of a gas if the temperature of the gas increases?
Answer in brief:
A gas in a cylinder is at pressure P. If the masses of all the molecules are made one-third of their original value and their speeds are doubled, then find the resultant pressure.
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
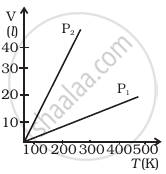
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 × 10 6 ms−1 and 1 × 106 ms−1, respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and t = 0.04, then the value of r is ______.
