Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
उत्तर
Given: Standard Temperature Pressure (S.T.P) i.e. T2 = 273 K, M01 (oxygen) = 32 × 10-3 kg/mol, M02 (helium) = 4 × 10-3 kg/mol,
`"v"_"rms" = sqrt("3RT"/"M"_0)`
The rms speed of oxygen molecules, `"v"_1 = sqrt("3RT"_1/"M"_01)` and that of helium molecules,
`"v"_2 = sqrt("3RT"_2/"M"_02)`
when v1 = v2 ,
`sqrt("3RT"_1/"M"_01) = sqrt("3RT"_2/"M"_02)`
`∴ "T"_1/"M"_01 = "T"_2/"M"_02`
∴ Temperature, T1 = `"M"_01/"M"_02. "T"_2`
`= ((32 xx 10^-3)(273))/(4 xx 10^-3)`
= 2184 K
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
When we place a gas cylinder on a van and the van moves, does the kinetic energy of the molecules increase? Does the temperature increase?
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
An ideal gas is trapped between a mercury column and the closed-end of a narrow vertical tube of uniform base containing the column. The upper end of the tube is open to the atmosphere. The atmospheric pressure equals 76 cm of mercury. The lengths of the mercury column and the trapped air column are 20 cm and 43 cm respectively. What will be the length of the air column when the tube is tilted slowly in a vertical plane through an angle of 60°? Assume the temperature to remain constant.
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
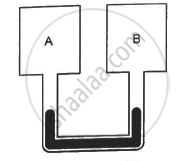
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Earth’s mean temperature can be assumed to be 280 K. How will the curve of blackbody radiation look like for this temperature? Find out λmax. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum, does this value lie? (Take Wien's constant b = 2.897 × 10−3 m K)
The number of degrees of freedom, for the vibrational motion of a polyatomic molecule, depends on the ______
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
Assuming the expression for the pressure exerted by the gas on the wall of the container, it can be shown that pressure is ______.
Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 × 10 6 ms−1 and 1 × 106 ms−1, respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity vo. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, at a given temperature, molecules of all gases have the same ______.
At what temperature will therms velocity of a gas be four times its value at STP?
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
Show that the average energy per molecule is proportional to the absolute temperature T of the gas.
