Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
उत्तर
Vrms = `sqrt((3"P")/ρ) = sqrt((3 xx 10^5)/(1.25))` = 489.89 m/s
Notes
[Note - Since density value given in question is of nitrogen, question is modified to obtain RMS velocity of nitrogen molecules.]
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Comment on the following statement: the temperature of all the molecules in a sample of a gas is the same.
A gas is kept in an enclosure. The pressure of the gas is reduced by pumping out some gas. Will the temperature of the gas decrease by Charles's low?
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
Find the number of molecules of an ideal gas in a volume of 1.000 cm3 at STP.
A gas cylinder has walls that can bear a maximum pressure of 1.0 × 106 Pa. It contains a gas at 8.0 × 105 Pa and 300 K. The cylinder is steadily heated. Neglecting any change in the volume, calculate the temperature at which the cylinder will break.
The temperature and pressure at Simla are 15.0°C and 72.0 cm of mercury and at Kalka these are 35.0°C and 76.0 cm of mercury. Find the ratio of air density at Kalka to the air density at Simla.
Use R=8.314J K-1 mol-1
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
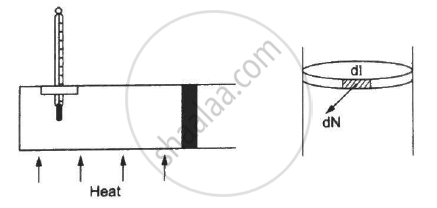
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area A fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is T0 and its pressure is p0 which equals the atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the tension in the wire? (b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to 2T0 ?

The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
Answer in brief:
What will happen to the mean square speed of the molecules of a gas if the temperature of the gas increases?
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
Under which condition laws of Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac are valid?
Compare the rate of radiation of metal bodies at 727 °C and 227 °C.
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
A ring of mass m and radius r rotates about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity `omega`. Its kinetic energy is ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
Two molecules of a gas have speeds of 9 × 10 6 ms−1 and 1 × 106 ms−1, respectively. What is the root mean square speed of these molecules?
For a particle moving in vertical circle, the total energy at different positions along the path ______.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
