Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Compare the rates of emission of heat by a blackbody maintained at 727°C and at 227°C, if the black bodies are surrounded by an enclosure (black) at 27°C. What would be the ratio of their rates of loss of heat?
Solution
Data: T1 = 273 + 727 = 1000 K,
T2 = 273 + 227 = 500 K,
T0 = 273 + 27 = 300 K
(i) The rate of emission of heat, `"dQ"/"dt" = sigma"AT"^4`.
We assume that the surface area A is the same for the two bodies.
`∴ ("dQ"//"dt")_1/("dQ"//"dt")_2 = "T"_1^4/"T"_2^4 = ("T"_1/"T"_2)^4`
`= (1000/500)^4 = 2^4 = 16`
(ii) The rate of loss of heat, `"dQ'"/"dt" = sigma"A" ("T"^4 - "T"_0^4)`
`∴ ("dQ'"//"dt")_1/("dQ'"//"dt")_2 = ("T"_1^4 - "T"_0^4)/("T"_2^4 - "T"_0^4)`
`= (10^12 - 81 xx 10^8)/(625 xx 10^8 - 81 xx 10^8)`
`= ((10000 - 81) xx 10^8)/(544 xx 10^8)`
`= 9919/544 = 18.23`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Can we define the temperature of (a) vacuum, (b) a single molecule?
A gas is kept in an enclosure. The pressure of the gas is reduced by pumping out some gas. Will the temperature of the gas decrease by Charles's low?
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
Which of the following quantities is the same for all ideal gases at the same temperature?
(a) The kinetic energy of 1 mole
(b) The kinetic energy of 1 g
(c) The number of molecules in 1 mole
(d) The number of molecules in 1 g
A gas cylinder has walls that can bear a maximum pressure of 1.0 × 106 Pa. It contains a gas at 8.0 × 105 Pa and 300 K. The cylinder is steadily heated. Neglecting any change in the volume, calculate the temperature at which the cylinder will break.
The mean speed of the molecules of a hydrogen sample equals the mean speed of the molecules of a helium sample. Calculate the ratio of the temperature of the hydrogen sample to the temperature of the helium sample.
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
0.040 g of He is kept in a closed container initially at 100.0°C. The container is now heated. Neglecting the expansion of the container, calculate the temperature at which the internal energy is increased by 12 J.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area A fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is T0 and its pressure is p0 which equals the atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the tension in the wire? (b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to 2T0 ?

Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

An adiabatic cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area 1 cm2 is closed at one end and fitted with a piston at the other end. The tube contains 0.03 g of an ideal gas. At 1 atm pressure and at the temperature of the surrounding, the length of the gas column is 40 cm. The piston is suddenly pulled out to double the length of the column. The pressure of the gas falls to 0.355 atm. Find the speed of sound in the gas at atmospheric temperature.
In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
Calculate the average molecular kinetic energy
- per kmol
- per kg
- per molecule
of oxygen at 127°C, given that the molecular weight of oxygen is 32, R is 8.31 J mol−1K−1 and Avogadro’s number NA is 6.02 × 1023 molecules mol−1.
Energy is emitted from a hole in an electric furnace at the rate of 20 W when the temperature of the furnace is 727°C. What is the area of the hole? (Take Stefan’s constant σ to be 5.7 × 10-8 Js-1 m-2K-4.)
Calculate the energy radiated in one minute by a blackbody of surface area 200 cm2 at 127 °C (σ = 5.7 x 10-8 J m-2 s-1 K-4)
A metal cube of length 4 cm radiates heat at the rate of 10 J/s. Find its emissive power at a given temperature.
What is the microscopic origin of temperature?
The average K.E. of hydrogen molecules at 27° C is E. The average K.E. at 627° C is ____________.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
Assuming the expression for the pressure exerted by the gas on the wall of the container, it can be shown that pressure is ______.
An ideal gas in a container of volume 500 cc is at a pressure of 2 × 105 N/m2. The average kinetic energy of each molecule is 6 × 10−21 J. The number of gas molecules in the container is ______.
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
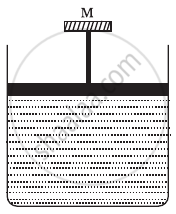
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity vo. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
When the temperature of an ideal gas is increased from 27°C to 227°C, its speed is changed from 400 ms-1 to vs, and Then vs is ______.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, at a given temperature, molecules of all gases have the same ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
