Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of average K.E.
Solution
The average K.E. will be the same, as conditions of temperature and pressure are the same.
Now as, `v_(rms) = sqrt((3pV)/M) = sqrt((3RT)/M)`
= `sqrt((3RT)/(mN)) = sqrt((3kT)/m)`
Where, M = Molar mass of the gas
m = Mass of each molecular of the gas
R = Gas constant
Clearly, `v_(rms) ∝ sqrt(1/m)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Consider a gas of neutrons. Do you expect it to behave much better as an ideal gas as compared to hydrogen gas at the same pressure and temperature?
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process `P = (P_0)/(1+(V/V_0)^2` where `p_0` and `V_0` are constants . Find the temperature of the gas when `V=V_0` .
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
If a = 0.72 and r = 0.24, then the value of tr is ______.
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
Above what temperature, all bodies radiate electromagnetic radiation?
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
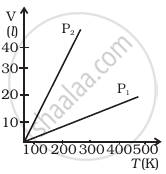
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
2000 calories of radiant heat is incident on a body. If the body absorbs 550 calories of heat, find the coefficient of emmission of the body.
