Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Why the temperature of all bodies remains constant at room temperature?
उत्तर
All bodies radiate as well as absorb radiation at room temperature, but their rate of emission and rate of absorption is the same, hence their temperature remains constant.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
A gas is kept in an enclosure. The pressure of the gas is reduced by pumping out some gas. Will the temperature of the gas decrease by Charles's low?
When you come out of a river after a dip, you feel cold. Explain.
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
A gas cylinder has walls that can bear a maximum pressure of 1.0 × 106 Pa. It contains a gas at 8.0 × 105 Pa and 300 K. The cylinder is steadily heated. Neglecting any change in the volume, calculate the temperature at which the cylinder will break.
One mole of an ideal gas undergoes a process `P = (P_0)/(1+(V/V_0)^2` where `p_0` and `V_0` are constants . Find the temperature of the gas when `V=V_0` .
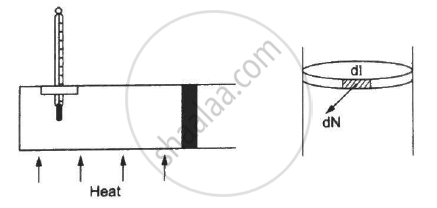
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
A glass contains some water at room temperature 20°C. Refrigerated water is added to it slowly. when the temperature of the glass reaches 10°C, small droplets condense on the outer surface. Calculate the relative humidity in the room. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 17.5 mm of mercury is 20°C and at 8.9 mm of mercury it is 10°C.
Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
When a gas is heated, its temperature increases. Explain this phenomenon on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases.
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Two vessels A and B are filled with the same gas where the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel A is twice the volume, temperature, and pressure in vessel B. Calculate the ratio of the number of molecules of the gas in vessel A to that in vessel B.
Calculate the value of λmax for radiation from a body having a surface temperature of 3000 K. (b = 2.897 x 10-3 m K)
Under which condition laws of Boyle, Charles, and Gay-Lussac are valid?
On what, the values of absorption coefficient, reflection coefficient, and transmission coefficient depend, in addition to the material of the object on which the radiation is an incident?
Above what temperature, all bodies radiate electromagnetic radiation?
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas becomes equal to 0.49 eV at a temperature about (Boltzmann constant = 1.38 x 10-23 JK-1) ____________.
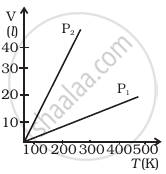
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
A gas mixture consists of molecules of types A, B and C with masses mA > mB > mC. Rank the three types of molecules in decreasing order of rms speeds.
Consider a rectangular block of wood moving with a velocity v0 in a gas at temperature T and mass density ρ. Assume the velocity is along x-axis and the area of cross-section of the block perpendicular to v0 is A. Show that the drag force on the block is `4ρAv_0 sqrt((KT)/m)`, where m is the mass of the gas molecule.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and t = 0.04, then the value of r is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
Show that the average energy per molecule is proportional to the absolute temperature T of the gas.
