Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
The condition of air in a closed room is described as follows. Temperature = 25°C, relative humidity = 60%, pressure = 104 kPa. If all the water vapour is removed from the room without changing the temperature, what will be the new pressure? The saturation vapour pressure at 25°C − 3.2 kPa.
उत्तर
Here ,
T = 298 K
RH = 60%
`"P" = 1.04 xx 10^5 "Pa"`
RH = `"Vapour pressure of water vapour" /"saturated Vapour pressure"`
=0.6
`"Saturated vapour pressure"= 3.2 xx 10^3 "Pa"`
⇒`"vapour pressure of water vapour" ("VP") = 0.6 xx 3.2 xx 10^3 = 1.92 xx 10^3 "Pa"`
If the water vapour is completely removed from the air , then net pressure = `1.04 xx 10^5 - 1.92 xx 10^3`
=`1.02 xx 10^5 "Pa"`
=102 kPa
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Do you expect the gas in a cooking gas cylinder to obey the ideal gas equation?
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
A gas is kept in an enclosure. The pressure of the gas is reduced by pumping out some gas. Will the temperature of the gas decrease by Charles's low?
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
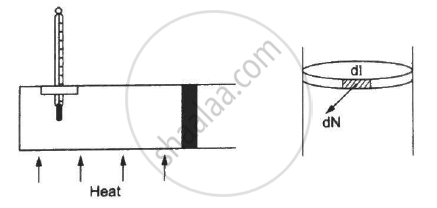
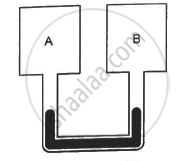
Figure shows two rigid vessels A and B, each of volume 200 cm3, containing an ideal gas (Cv = 12.5 J K−1 mol−1). The vessels are connected to a manometer tube containing mercury. The pressure in both the vessels is 75 cm of mercury and the temperature is 300 K. (a) Find the number of moles of the gas in each vessel. (b) 5.0 J of heat is supplied to the gas in vessel A and 10 J to the gas in vessel B. Assuming there's no appreciable transfer of heat from A to B, calculate the difference in the heights of mercury in the two sides of the manometer. Gas constant, R = 8.3 J K−1 mol−1.
Answer in brief:
Compare the rms speed of hydrogen molecules at 127ºC with rms speed of oxygen molecules at 27ºC given that molecular masses of hydrogen and oxygen are 2 and 32 respectively.
If the density of oxygen is 1.44 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 N/m2, find the root mean square velocity of oxygen molecules.
The emissive power of a sphere of area 0.02 m2 is 0.5 kcal s-1m-2. What is the amount of heat radiated by the spherical surface in 20 seconds?
If the density of nitrogen is 1.25 kg/m3 at a pressure of 105 Pa, find the root mean square velocity of nitrogen molecules.
Explain in detail the kinetic interpretation of temperature.
A ring of mass m and radius r rotates about an axis passing through its centre and perpendicular to its plane with angular velocity `omega`. Its kinetic energy is ______.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
The average translational kinetic energy of a molecule in a gas is 'E1'. The kinetic energy of the electron (e) accelerated from rest through p.d. 'V' volt is 'E2'. The temperature at which E1 = E2 is possible, is ______.
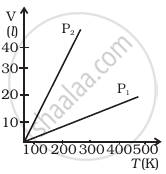
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
The molecules of a given mass of a gas have root mean square speeds of 100 ms−1 at 27°C and 1.00 atmospheric pressure. What will be the root mean square speeds of the molecules of the gas at 127°C and 2.0 atmospheric pressure?
The Q-value of a nuclear reaction and kinetic energy of the projectile particle, KP are related as ______.
A proton, a deuteron and an α-particle with same kinetic energy enter into a uniform magnetic field at right angle to magnetic field. The ratio of the radii of their respective circular paths is ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
Assuming the expression for the pressure P exerted by an ideal gas, prove that the kinetic energy per unit volume of the gas is `3/2` P.
