Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
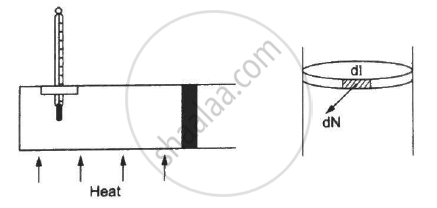
उत्तर
Here ,
`P_1 = 10^5 "Pa"`
`A = π(0.05)^2`
L = 0.2 m
`V = AL = 0.0016 \text ( m)^3`
`T_1 = 300 K`
`T_2 = 600 K `
`µ = 0.20`
Applying 5 variable equation of state , we get
`(P_1V)/T_1 = (P_2V)/T_2`
⇒ `P_1/T_1 = P_2/T_2`
⇒ `P_2 = T_2/T_1 × P_1 = 600/300 × 10^5`
⇒ `P_2 = 2 × 10^5`
Net pressure , `P = P_2 - P_1 = 2 × 10^5 - 10^5 = 10^5`
Total force acting on the stopper = `PA = 10^5×pi×(0.05)^2`
Applying law of friction , we get
`F = µN = 0.2N`
⇒ `N = F/µ = (10^5×pi×(0.05)^2)/0.2`
`(dN)/(dl) = N/(2pir) = (10^5×pi×(0.05)^2)/(0.2×2pi×(0.05))=0.125×10^5`
⇒ `(dN)/(dl) = 1.25×10^4 N/m`
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
Is it possible to boil water at room temperature, say 30°C? If we touch a flask containing water boiling at this temperature, will it be hot?
Which of the following parameters is the same for molecules of all gases at a given temperature?
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
The average translational kinetic energy of air molecules is 0.040 eV (1 eV = 1.6 × 10−19J). Calculate the temperature of the air. Boltzmann constant k = 1.38 × 10−23 J K−1.
An ideal gas is kept in a long cylindrical vessel fitted with a frictionless piston of cross-sectional area 10 cm2 and weight 1 kg in figure. The vessel itself is kept in a big chamber containing air at atmospheric pressure 100 kPa. The length of the gas column is 20 cm. If the chamber is now completely evacuated by an exhaust pump, what will be the length of the gas column? Assume the temperature to remain constant throughout the process.
The weather report reads, "Temperature 20°C : Relative humidity 100%". What is the dew point?
Using figure, find the boiling point of methyl alcohol at 1 atm (760 mm of mercury) and at 0.5 atm.

A glass contains some water at room temperature 20°C. Refrigerated water is added to it slowly. when the temperature of the glass reaches 10°C, small droplets condense on the outer surface. Calculate the relative humidity in the room. The boiling point of water at a pressure of 17.5 mm of mercury is 20°C and at 8.9 mm of mercury it is 10°C.
Answer in brief:
Show that rms velocity of an oxygen molecule is `sqrt2` times that of a sulfur dioxide molecule at S.T.P.
In an ideal gas, the molecules possess
Explain, on the basis of the kinetic theory of gases, how the pressure of a gas changes if its volume is reduced at a constant temperature.
Average kinetic energy of H2 molecule at 300K is 'E'. At the same temperature, average kinetic energy of O2 molecule will be ______.
A molecule consists of two atoms each of mass 'm' and separated by a distance 'd'. At room temperature the average rotational kinetic energy is 'E', then its angular frequency is ______.
A cylinder containing an ideal gas is in vertical position and has a piston of mass M that is able to move up or down without friction (Figure). If the temperature is increased ______.
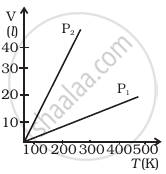
Volume versus temperature graphs for a given mass of an ideal gas are shown in figure at two different values of constant pressure. What can be inferred about relation between P1 and P2?
An inflated rubber balloon contains one mole of an ideal gas, has a pressure p, volume V and temperature T. If the temperature rises to 1.1 T, and the volume is increased to 1.05 V, the final pressure will be ______.
When a particle oscillates simple harmonically, its kinetic energy varies periodically. If frequency of the particle is n, then the frequency of the kinetic energy is ______.
If a = 0. 72 and r = 0.24, then the value of t is ______.
