Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
A gas is kept in an enclosure. The pressure of the gas is reduced by pumping out some gas. Will the temperature of the gas decrease by Charles's low?
उत्तर
If the gas is ideal, there will be no temperature change. Moreover, Charles's law relates volume with temperature not pressure with temperature, so the cause behind the phenomena cannot be explained by Charles's law.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
It is said that the assumptions of kinetic theory are good for gases having low densities. Suppose a container is so evacuated that only one molecule is left in it. Which of the assumptions of kinetic theory will not be valid for such a situation? Can we assign a temperature to this gas?
If the molecules were not allowed to collide among themselves, would you expect more evaporation or less evaporation?
The mean square speed of the molecules of a gas at absolute temperature T is proportional to
The process on an ideal gas, shown in figure, is
A gas cylinder has walls that can bear a maximum pressure of 1.0 × 106 Pa. It contains a gas at 8.0 × 105 Pa and 300 K. The cylinder is steadily heated. Neglecting any change in the volume, calculate the temperature at which the cylinder will break.
At what temperature the mean speed of the molecules of hydrogen gas equals the escape speed from the earth?
Use R = 8.314 JK-1 mol-1
Air is pumped into the tubes of a cycle rickshaw at a pressure of 2 atm. The volume of each tube at this pressure is 0.002 m3. One of the tubes gets punctured and the volume of the tube reduces to 0.0005 m3. How many moles of air have leaked out? Assume that the temperature remains constant at 300 K and that the air behaves as an ideal gas.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
During an experiment, an ideal gas is found to obey an additional law pV2 = constant. The gas is initially at a temperature T and volume V. Find the temperature when it expands to a volume 2V.
Use R = 8.3 J K-1 mol-1
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of radius 5 cm and length 20 cm. It is closed by a tight-fitting cork. The friction coefficient between the cork and the tube is 0.20. The tube contains an ideal gas at a pressure of 1 atm and a temperature of 300 K. The tube is slowly heated and it is found that the cork pops out when the temperature reaches 600 K. Let dN denote the magnitude of the normal contact force exerted by a small length dlof the cork along the periphery (see the figure). Assuming that the temperature of the gas is uniform at any instant, calculate `(dN)/(dt)`.
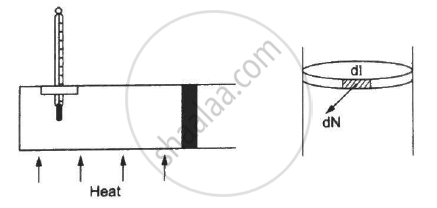
Figure shows a cylindrical tube of cross-sectional area A fitted with two frictionless pistons. The pistons are connected to each other by a metallic wire. Initially, the temperature of the gas is T0 and its pressure is p0 which equals the atmospheric pressure. (a) What is the tension in the wire? (b) What will be the tension if the temperature is increased to 2T0 ?

At what temperature will oxygen molecules have same rms speed as helium molecules at S.T.P.? (Molecular masses of oxygen and helium are 32 and 4 respectively).
Find the kinetic energy of 5 litres of a gas at STP, given the standard pressure is 1.013 × 105 N/m2.
Earth’s mean temperature can be assumed to be 280 K. How will the curve of blackbody radiation look like for this temperature? Find out λmax. In which part of the electromagnetic spectrum, does this value lie? (Take Wien's constant b = 2.897 × 10−3 m K)
The power radiated by a perfect blackbody depends only on its ______
An insulated container containing monoatomic gas of molar mass m is moving with a velocity vo. If the container is suddenly stopped, find the change in temperature.
Two gases A and B are at absolute temperatures of 360 K and 420 K, respectively. The ratio of the average kinetic energy of the molecules of gas B to that of gas A is ______.
According to the kinetic theory of gases, at a given temperature, molecules of all gases have the same ______.
Which of the following materials is diathermanous?
Show that the average energy per molecule is proportional to the absolute temperature T of the gas.
