Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
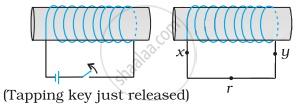
Solution
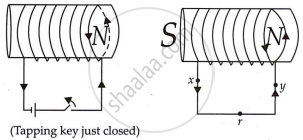
Lenz's law specifies the direction of the induced current in a closed loop. Using Lenz’s rule, the direction of the induced current in the given situation can be predicted as follows:
The induced current in the right coil drives X to Y.
The direction of the induced current is along the xryx.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Describe a simple experiment (or activity) to show that the polarity of emf induced in a coil is always such that it tends to produce a current which opposes the change of magnetic flux that produces it.
Consider the situation shown in figure. If the switch is closed and after some time it is opened again, the closed loop will show ____________ .
A bar magnet is dropped through a copper ring acceleration of magnet is
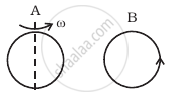
There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that ______.

Same as problem 4 except the coil A is made to rotate about a vertical axis (figure). No current flows in B if A is at rest. The current in coil A, when the current in B (at t = 0) is counterclockwise and the coil A is as shown at this instant, t = 0, is ______.
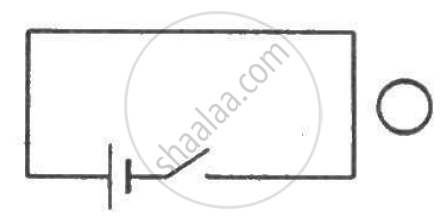
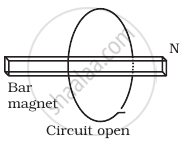
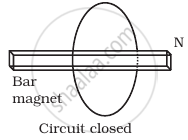
Consider a magnet surrounded by a wire with an on/off switch S (Figure). If the switch is thrown from the off position (open circuit) to the on position (closed circuit), will a current flow in the circuit? Explain.
A solenoid is connected to a battery so that a steady current flows through it. If an iron core is inserted into the solenoid, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
A metallic ring of mass m and radius `l` (ring being horizontal) is falling under gravity in a region having a magnetic field. If z is the vertical direction, the z-component of magnetic field is Bz = Bo (1 + λz). If R is the resistance of the ring and if the ring falls with a velocity v, find the energy lost in the resistance. If the ring has reached a constant velocity, use the conservation of energy to determine v in terms of m, B, λ and acceleration due to gravity g.
A long solenoid ‘S’ has ‘n’ turns per meter, with diameter ‘a’. At the centre of this coil we place a smaller coil of ‘N’ turns and diameter ‘b’ (where b < a). If the current in the solenoid increases linearly, with time, what is the induced emf appearing in the smaller coil. Plot graph showing nature of variation in emf, if current varies as a function of mt2 + C.
