Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
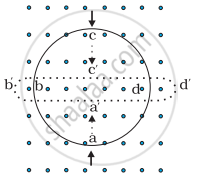
Consider the situation shown in figure. If the switch is closed and after some time it is opened again, the closed loop will show ____________ .
Options
an anticlockwise current-pulse
a clockwise current-pulse
an anticlockwise current-pulse and then a clockwise current-pulse
a clockwise current-pulse and then an anticlockwise current-pulse
Solution
a clockwise current-pulse and then an anticlockwise current-pulse
When the switch is closed, the current will flow in downward direction in part AB of the circuit nearest to the closed loop.
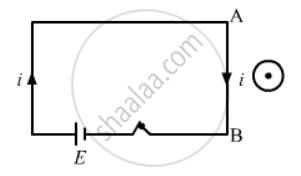
Due to current in wire AB, a magnetic field will be produced in the loop. This magnetic field due to increasing current will be the cause of the induced current in the closed loop. According to Lenz's law, the induced current is such that it opposes the increase in the magnetic field that induces it. So, the induced current will be in clockwise direction opposing the increase in the magnetic field in upward direction.
Similarly, when the circuit is opened, the current will suddenly fall in the circuit, leading to decrease in the magnetic field in the loop. Again, according to Lenz's law, the induced current is such that it opposes the decrease in the magnetic field. So, the induced current will be in anti-clockwise direction, opposing the decrease in the magnetic field in upward direction.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State Lenz's law. Illustrate, by giving an example, how this law helps in predicting the direction of the current in a loop in the presence of a changing magnetic flux.
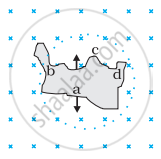
Use Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current in the situation described by the figure:
A wire of irregular shape turning into a circular shape.
What is the direction of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 when current I in the wire is increasing steadily?
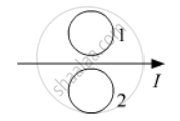
Predict the directions of induced currents in metal rings 1 and 2 lying in the same plane where current I in the wire is increasing steadily.
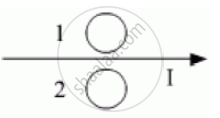
A bar magnet is moved in the direction indicated by the arrow between two coils PQ and CD. Predict the directions of induced current in each coil.
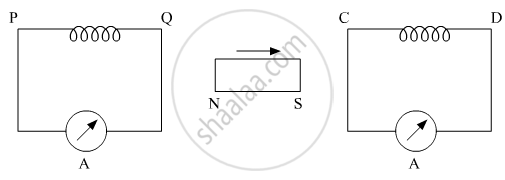
The battery discussed in the previous question is suddenly disconnected. Is a current induced in the other loop? If yes, when does it start and when does it end? Do the loops attract each other or repel?
Two circular loops of equal radii are placed coaxially at some separation. The first is cut and a battery is inserted in between to drive a current in it. The current changes slightly because of the variation in resistance with temperature. During this period, the two loops _______________ .
Explain, with the help of a suitable example, how we can show that Lenz's law is a consequence of the principle of conservation of energy.
Lenz’s law is a consequence of the law of conservation of ______.
2 A 40 kg boy whose legs are 4 cm in area and 50 cm long falls through a height of 2 m without breaking his leg bones. If the bones can withstand stress of 0.9 x 108 N/m2. The Young's modulus for the material of the bone is ______.
Young's modulus for aluminium is 7 × 1010 Pa. The force needed to stretch an aluminium wire of diameter 2 mm and length 800 mm by 1 mm is ______.
There are two coils A and B as shown in figure. A current starts flowing in B as shown, when A is moved towards B and stops when A stops moving. The current in A is counterclockwise. B is kept stationary when A moves. We can infer that ______.

A wire in the form of a tightly wound solenoid is connected to a DC source, and carries a current. If the coil is stretched so that there are gaps between successive elements of the spiral coil, will the current increase or decrease? Explain.
Consider a metal ring kept on top of a fixed solenoid (say on a carboard) (Figure). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current is suddenly switched on, the metal ring jumps up. Explain
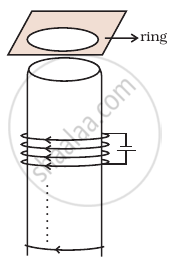
Consider a metal ring kept (supported by a cardboard) on top of a fixed solenoid carrying a current I (Figure). The centre of the ring coincides with the axis of the solenoid. If the current in the solenoid is switched off, what will happen to the ring?

A long solenoid ‘S’ has ‘n’ turns per meter, with diameter ‘a’. At the centre of this coil we place a smaller coil of ‘N’ turns and diameter ‘b’ (where b < a). If the current in the solenoid increases linearly, with time, what is the induced emf appearing in the smaller coil. Plot graph showing nature of variation in emf, if current varies as a function of mt2 + C.
Predict the direction of induced current in the situation described by the following figure.
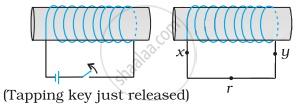
Use Lenz’s law to determine the direction of induced current in the situation described by the figure.
A circular loop being deformed into a narrow straight wire.