Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Predict the major product (s) of the following reactions and explain their formation.
\[\ce{H3C - CH = CH2 ->[(Ph.CO.O)2][HBr]}\]
\[\ce{H3C - CH = CH2 ->[HBr]}\]
Solution
Addition of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes follows Markonikov rule. It states that negative part of the addendum (adding molecule) gets attached to that carbon atom which possesses lesser number of hydrogen atoms.
Mechanism: Hydrogen bromide provides an electrophile, H+, which attacks the double bond to form carbocation as shown below:
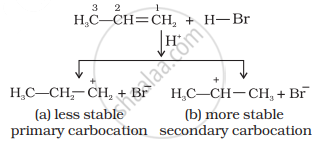
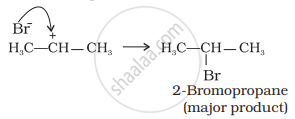
The (b) is attacked by Br– ion to form the product as follows:
Addition reaction of HBr to unsymmetrical alkenes in the presence of peroxide follows anti-Markovnikov rule.
Mechanism: Peroxide effect proceeds via free radical chain mechanism as given below:
(i)
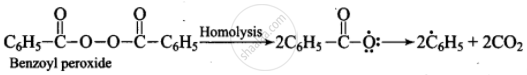
(ii) \[\ce{\overset{\bullet}{C6}H5 + H - Br ->[Homolysis] C6H6 + \overset{\bullet}{B}r}\]
(iii)
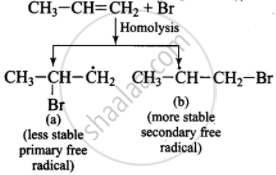
(iv) \[\ce{CH3 - \overset{\bullet}{C}H - CH2Br + H - Br ->[Homolysis] \underset{(major product)}{CH3 - CH2 - CH2Br + Br}}\]
\[\ce{H3C - CH = CH2 ->[(PhCOO)2][HBr] \underset{(Anti-Markovnikov addition)}{H3CCH2CH2Br}}\]
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H3C - CH = CH2 ->[HBr] H3C - CH - CH3}\\
\phantom{......................}|\\
\phantom{.......................}\ce{\underset{(Markovnikov addition)}{Br}}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Which of the following reactions of methane is incomplete combustion:
The intermediate carbocation formed in the reactions of HI, HBr and HCl with propene is the same and the bond energy of HCl, HBr and HI is 430.5 kJ mol–1, 363.7 kJ mol–1 and 296.8 kJ mol–1 respectively. What will be the order of reactivity of these halogen acids?
Nucleophiles and electrophiles are reaction intermediates having electron-rich and electron-deficient centres respectively. Hence, they tend to attack electron-deficient and electron-rich centres respectively. Classify the following species as electrophiles and nucleophiles.
(i) H3CO–
(ii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.}\ce{O}\\
\phantom{.}||\\
\ce{H3C - C - O-}
\end{array}\]
(iii) \[\ce{\overset{\bullet}{C}l}\]
(iv) Cl2C:
(v) (H3C)3C+
(vi) Br–
(vii) H3COH
(viii) R – NH – R
Write hydrocarbon radicals that can be formed as intermediates during monochlorination of 2-methylpropane? Which of them is more stable? Give reasons.
Complete combustion of 750 g of an organic compound provides 420 g of CO2 and 210 g of H2O. The percentage composition of carbon and hydrogen in organic compound is 15.3 and ______ respectively. (Round off to the Nearest Integer).
What would be the product when neopentyl chloride reacts with sodium ethoxide?
