Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Repeat part (a) of problem 6 if the push is applied horizontally and not parallel to the incline.
Solution
Using the free body diagram,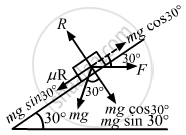
g = 10 m/s2, m = 2 kg, θ = 30 and μ = 0.2
R − mg cos θ − F sin θ = 0
⇒ R = mg cos θ + F sin θ (1)
and
mg sin θ + μR − F cos θ = 0
⇒ mg sin θ + μ(mg cos θ + F sin θ) − F cos θ = 0
⇒ mg sin θ + μmg cos θ + μF sin θ − F cos θ = 0
`=>F=(mg sintheta+mu mgcostheta)/(musintheta-costheta)(theta=30^circ)`
`=(2xx20xx(1/2)+0.2xx2xx10xxsqrt3/2)/(0.2xx(1/2)-(sqrt3/2)`
`13.464/0.76=17.7`N = 17.5 N
Therefore, while pushing the block to move up on the incline, the required force is 17.5 N.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A block A kept on an inclined surface just begins to slide if the inclination is 30°. The block is replaced by another block B and it is found that it just begins to slide if the inclination is 40°.
The contact force exerted by a body A on another body B is equal to the normal force between the bodies We conclude that
(a) the surface must be frictionless
(b) the force of friction between the bodies is zero
(c) the magnitude of normal force equal that of friction
(d) the bodies may be rough but they don't slip on each other.
A body slipping on a rough horizontal plane moves with a deceleration of 4.0 m/s2. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the plane?
A block of mass m is kept on a horizontal table. If the static friction coefficient is μ, find the frictional force acting on the block.
A block slides down an inclined surface of inclination 30° with the horizontal. Starting from rest it covers 8 m in the first two seconds. Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the two.
The angle between the resultant contact force and the normal force exerted by a body on the other is called the angle of friction. Show that, if λ be the angle of friction and μ the coefficient of static friction λ ≤ tan−1 μ.
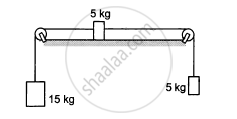
If the tension in the string in the following figure is 16 N and the acceleration of each block is 0.5 m/s2, find the friction coefficients at the two contact with the blocks.
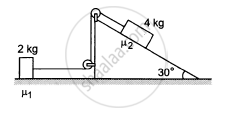
The friction co-efficient between the table and the block shown in the following figure is 0.2. Find the tensions in the two strings.
The friction coefficient between an athelete's shoes and the ground is 0.90. Suppose a superman wears these shoes and races for 50 m. There is no upper limit on his capacity of running at high speeds. (a) Find the minimum time that he will have to take in completing the 50 m starting from rest. (b) Suppose he takes exactly this minimum time to complete the 50 m, what minimum time will he take to stop?
Two masses M1 and M2 are connected by a light rod and the system is slipping down a rough incline of angle θ with the horizontal. The friction coefficient at both the contacts is μ. Find the acceleration of the system and the force by the rod on one of the blocks.
A block of mass M is kept on a rough horizontal surface. The coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface is μ. The block is to be pulled by applying a force to it. What minimum force is needed to slide the block? In which direction should this force act?
A 2 kg block is placed over a 4 kg block and both are placed on a smooth horizontal surface. The coefficient of friction between the block is 0.20. Find the acceleration of the two blocks if a horizontal force of 12 N is applied to (a) the upper block, (b) the lower block. Take g = 10 m/s2.
The friction coefficient between the two blocks shown in the following figure is μ but the floor is smooth. (a) What maximum horizontal force F can be applied without disturbing the equilibrium of the system? (b) Suppose the horizontal force applied is double of that found in part (a). Find the accelerations of the two masses.
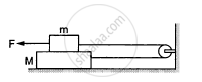
Suppose the entire system of the previous questions is kept inside an elevator which is coming down with an acceleration a < g. Repeat parts (a) and (b).
A block of mass m slips on a rough horizontal table under the action of a horizontal force applied to it. The coefficient of friction between the block and the table is μ. The table does not move on the floor. Find the total frictional force applied by the floor on the legs of the table. Do you need the friction coefficient between the table and the floor or the mass of the table?
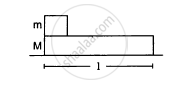
In the following figure shows a small block of mass m kept at the left end of a larger block of mass M and length l. The system can slide on a horizontal road. The system is started towards right with an initial velocity v. The friction coefficient between the road and the bigger block is μ and that between the block is μ/2. Find the time elapsed before the smaller blocks separates from the bigger block.
A block placed on a rough horizontal surface is pulled by a horizontal force F. Let f be the force applied by the rough surface on the block. Plot a graph of f versus F.
The coefficient of static friction between a wooden block of mass 0.5 kg and a vertical rough wall is 0.2. The magnitude of horizontal force that should be applied on the block to keep it adhered to the wall will be ______ N. [g = 10 ms-2]
An inclined plane is bent in such a way that the vertical cross-section is given by Y = `x^2/4` where y is in vertical and x in horizontal direction. If the upper surface of this curved plane is rough with coefficient of friction µ = 0.5, the maximum height in cm at which a stationary block will not slip downward is ______ cm.
