Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solve the following example.
Doctor has prescribed a lens having power +1.5 D. What will be the focal length of the lens? What is the type of the lens and what must be the defect of vision?
Solution
Given:
Power of lens, P = +1.5 D
Now, focal length of lens, \[f = \frac{1}{P} = + \frac{1}{1 . 5} = + 0 . 67 m\]
Since, the focal length is positive, the lens prescribed for correction is convex lens. Thus, the defect of vision is farsightedness or hypermetropia.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Make a diagram to show how hypermetropia is corrected. The near point of a hypermetropic eye is 1 m. What is the power of the lens required to correct this defect? Assume that the near point of the normal eye is 25 cm.
Name the defect shown in the diagram.
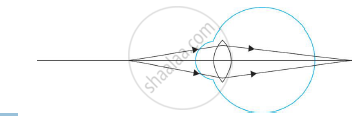
In hypermetropia human eye _______.
 : Concave lens : :
: Concave lens : : 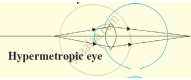 : ______
: ______
Find the odd one out and give its explanation.
Hypermetropia can be corrected using concave lens of proper focal length.
Write scientific reason.
Farsightedness, this defect can be corrected by using convex lens.
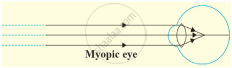
The defect of vision in which the person is able to see a distant object distinctly but cannot see nearby objects clearly is called:
Assertion: The near point of a hypermetropia eye is more than 25 cm away.
Reason: Hypermetropia is corrected using spectacles containing concave lenses.
Draw ray diagram showing hypermetropic eye.
List two difference in the characteristic properties of the virtual images formed by the two types of spherical lenses (concave and convex). How are these characteristics of the two lenses use in the correction of the two common defects of vision namely myopia and hypermetropia?
Differentiate between members of the following pair with reference to what is asked in the bracket.
Myopia and Hyperopia (type of lens used for correction).
