Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State Kirchhoff ’s voltage rule.
Solution
It states that in a closed circuit the algebraic sum of the products of the current and resistance of each part of the circuit is equal to the total emf included in the circuit. This rule follows from the law of conservation of energy for an isolated system.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
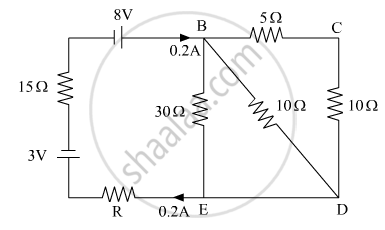
Calculate the value of the resistance R in the circuit shown in the figure so that the current in the circuit is 0.2 A. What would b the potential difference between points B and E?
A capacitor of capacitance 8.0 μF is connected to a battery of emf 6.0 V through a resistance of 24 Ω. Find the current in the circuit (a) just after the connections are made and (b) one time constant after the connections are made.
State and explain Kirchhoff’s rules.
Kirchhoff’s second law is a consequence of law of conservation of ______.
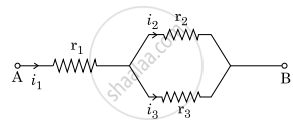
Three resistors having resistances r1, r2 and r3 are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio `"i"_3/"i"_1` of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is :
What are the advantages of the null-point method in a Wheatstone bridge? What additional measurements would be required to calculate `R_(unknown)` by any other method?
Power P is to be delivered to a device via transmission cables having resistance RC. If V is the voltage across R and I the current through it, find the power wasted and how can it be reduced.
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in the analysis of electric circuits and explain them.
A 6-volt battery is connected to the terminals of a three-metre-long wire of uniform thickness and resistance of 100 ohms. The difference of potential between two points on the wire separated by a distance of 50 cm will be ______.
The figure below shows two batteries, E1 and E2, having emfs of 18V and 10V and internal resistances of 1 Ω and 2 Ω, respectively. W1, W2 and W3 are uniform metallic wires AC, FD and BE having resistances of 8 Ω, 6 Ω and 10 Ω respectively. B and E are midpoints of the wires W1 and W2. Using Kirchhoff's laws of electrical circuits, calculate the current flowing in the wire W3:

