Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the advantages of the null-point method in a Wheatstone bridge? What additional measurements would be required to calculate `R_(unknown)` by any other method?
Solution
The advantage of the null point method in a Wheatstone bridge is that the resistance of galvanometer does not affect the balance point and there is no need to determine the current in resistances and galvanometer and the internal resistance of a galvanometer. `R_(unknown)` can be calculated by applying Kirchhoff’s rules to the circuit. We would need additional accurate measurements of all the currents in resistances and galvanometer and internal resistance of the galvanometer.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in electric networks. How are there rules justified?
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of (11/3) Ω?
Consider the potentiometer circuit as arranged in the figure. The potentiometer wire is 600 cm long. (a) At what distance from the point A should the jockey touch the wire to get zero deflection in the galvanometer? (b) If the jockey touches the wire at a distance of 560 cm from A, what will be the current in the galvanometer?
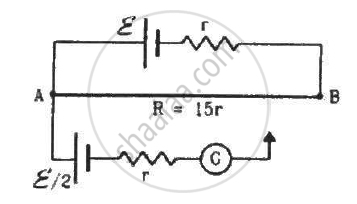
On which conservation principle is Kirchoff's Second Law of electrical networks based?
State Kirchhoff ’s voltage rule.
State and explain Kirchhoff’s rules.
A potentiometer wire has a length of 4 m and resistance of 20 Ω. It is connected in series with resistance of 2980 Ω and a cell of emf 4 V. Calculate the potential along the wire.
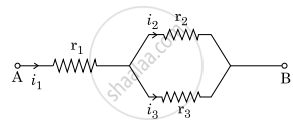
Three resistors having resistances r1, r2 and r3 are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio `"i"_3/"i"_1` of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is :
In a meter bridge the point D is a neutral point (Figure).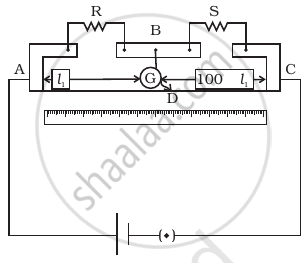
- The meter bridge can have no other neutral point for this set of resistances.
- When the jockey contacts a point on meter wire left of D, current flows to B from the wire.
- When the jockey contacts a point on the meter wire to the right of D, current flows from B to the wire through galvanometer.
- When R is increased, the neutral point shifts to left.
Derive the equation of the balanced state in a Wheatstone bridge using Kirchhoff’s laws.
