Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the two Kirchhoff’s rules used in the analysis of electric circuits and explain them.
Solution
- Junction rule: At any junction, the sum of the currents entering the junction is equal to the sum of currents leaving the junction.
- Loop rule: The algebraic sum of changes in potential around any closed loop involving resistors and cells in the loop is zero.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Given the resistances of 1 Ω, 2 Ω, 3 Ω, how will be combine them to get an equivalent resistance of 6 Ω?
Determine the equivalent resistance of networks shown in Fig.
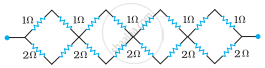
In the given circuit, assuming point A to be at zero potential, use Kirchhoff’s rules to determine the potential at point B.

Consider the following two statements:-
(A) Kirchhoff's junction law follows from conservation of charge.
(B) Kirchhoff's loop law follows from conservative nature of electric field.
Consider the potentiometer circuit as arranged in the figure. The potentiometer wire is 600 cm long. (a) At what distance from the point A should the jockey touch the wire to get zero deflection in the galvanometer? (b) If the jockey touches the wire at a distance of 560 cm from A, what will be the current in the galvanometer?
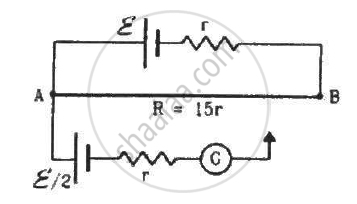
On which conservation principle is Kirchoff's Second Law of electrical networks based?
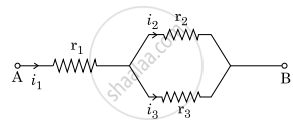
Three resistors having resistances r1, r2 and r3 are connected as shown in the given circuit. The ratio `"i"_3/"i"_1` of currents in terms of resistances used in the circuit is :
Why are alloys used for making standard resistance coils?
Derive the equation of the balanced state in a Wheatstone bridge using Kirchhoff’s laws.
