Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
State the principle of an ac generator and explain its working with the help of a labelled diagram. Obtain the expression for the emf induced in a coil. having N turns each of cross-sectional area A, rotating with a constant angular speed 'ω' in a magnetic field `vecB` directed perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
Solution
Principle - Based on the phenomenon of electromagnetic induction
Construction

Main parts of an ac generator:
Armature − Rectangular coil ABCD
Filed Magnets − Two pole pieces of a strong electromagnet
Slip Rings − The ends of coil ABCD are connected to two hollow metallic rings R1 and R2
Brushes − B1 and B2 are two flexible metal plates or carbon rods. They are fixed and are kept in tight contact with R1 and R2 respectively.
Theory and Working − As the armature coil is rotated in the magnetic field, angle θ between the field and normal to the coil changes continuously. Therefore, magnetic flux linked with the coil changes. An emf is induced in the coil. According to Fleming’s right-hand rule, current induced in AB is from A to B and it is from C to D in the CD. In the external circuit, current flows from B2 to B1
To calculate the magnitude of emf induced:
Suppose
A → Area of each turn of the coil
N → Number of turns in the coil
`vecB`→ Strength of magnetic field
θ → Angle which normal to the coil makes with `vecB` at any instant t
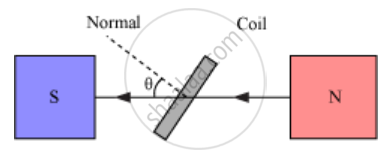
∴ Magnetic flux linked with the coil in this position:
`phi = N(vecB.vecA)` = NBA cosθ= NBA cosωt …(i)
Where ‘ω’ is angular velocity of the coil
As the coil rotates, angle θ changes. Therefore, magnetic flux Φ linked with the coil changes and hence, an emf is induced in the coil. At this instant t, if e is the emf induced in the coil, then
`e = -(dtheta)/(dt) = - d/(dt) (NAB cos omegat)`
`= -NAB d/(dt) (cos omegat)`
`=-NAB(-sin omegat)omega`
∴ e = NAB ω sinωt
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Suppose the loop is stationary but the current feeding the electromagnet that produces the magnetic field is gradually reduced so that the field decreases from its initial value of 0.3 T at the rate of 0.02 T s−1. If the cut is joined and the loop has a resistance of 1.6 Ω how much power is dissipated by the loop as heat? What is the source of this power?
Describe briefly, with the help of a labelled diagram, the basic elements of an A.C. generator.
The instantaneous values of alternating current and voltage in a circuit are
i = `1/sqrt2` sin 100π A and
v = `1/sqrt2 sin (100 pi"t" + pi/3)"V"`.
The average power in watts consumed in the circuit is
Give the principle of AC generator.
List out the advantages of stationary armature-rotating field system of AC generator.
Define average value of an alternating current.
A resistor, capacitor, and inductor are connected in series across an AC generator. Which of the following statements is false?
In an A.C circuit, the current
When the speed of a d.c. motor increases the armature current ______
Obtain the expression for the instantaneous value of emf induced.
