Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Suggest and describe a technique to obtain multiple copies of a gene of interest in vitro.
Solution
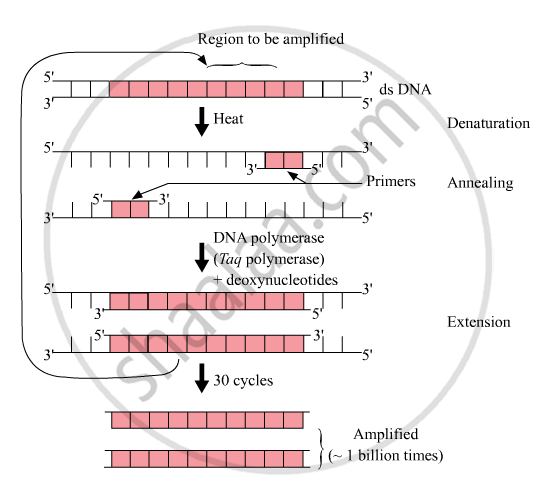
For the PCR, two sets of primers (chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to a region of DNA), the enzyme DNA polymerase and deoxynucleotides are added.
The PCR consists of three steps:
-
Denaturation: Double helical DNA is denatured at a high temperature. DNA polymerase does not get degraded at this temperature, as the DNA polymerase used in this reaction is thermostable. It is isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus (Taq).
-
Annealing: It is the step in which primers are annealed to single-stranded DNA templates. Two sets of primers (chemically synthesised small oligonucleotides that are
complementary to the regions of DNA) are used. The temperature of the reaction mixture is lowered to 50–65 °C for some seconds to allow annealing of the primers. DNA polymerase extends the primer in the 5' to 3' direction. -
Extension: Replication of DNA occurs in vitro.
-
This cycle is repeated several times to generate up to one billion identical copies of DNA.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name two commonly used bioreactors.
Explain briefly:
Chitinase
Answer the following question:
Describe the formation of recombinant DNA by the action of EcoRI.
PCR proceeds mthree distinct steps governed by temperature, they are in order of ______.
During the purification process for recombinant DNA technology, the addition of chilled ethanol precipitates out ______.
An antibiotic resistance gene in a vector usually helps in the selection of ______.
Significance of 'heat shock' method in bacterial transformation is to facilitate ______.
A bacterial cell was transformed with a recombinant DNA molecule that was generated using a human gene. However, the transformed cells did not produce the desired protein. Reasons could be ______.
While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
Illustrate the design of a bioreactor. Highlight the difference between a flask in your laboratory and a bioreactor which allows cells to grow in a continuous culture system.
