Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suggest and describe a technique to obtain multiple copies of a gene of interest in vitro.
उत्तर
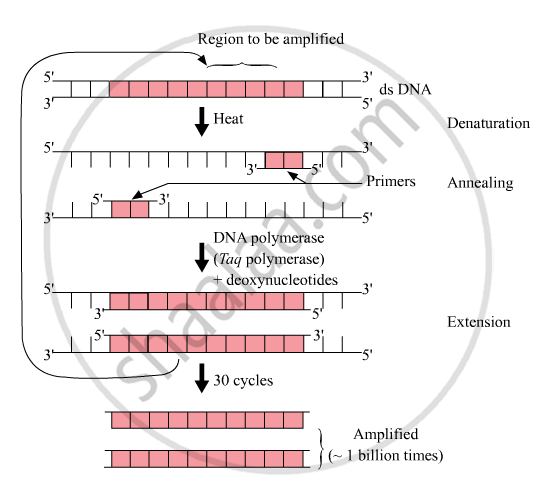
For the PCR, two sets of primers (chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to a region of DNA), the enzyme DNA polymerase and deoxynucleotides are added.
The PCR consists of three steps:
-
Denaturation: Double helical DNA is denatured at a high temperature. DNA polymerase does not get degraded at this temperature, as the DNA polymerase used in this reaction is thermostable. It is isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus (Taq).
-
Annealing: It is the step in which primers are annealed to single-stranded DNA templates. Two sets of primers (chemically synthesised small oligonucleotides that are
complementary to the regions of DNA) are used. The temperature of the reaction mixture is lowered to 50–65 °C for some seconds to allow annealing of the primers. DNA polymerase extends the primer in the 5' to 3' direction. -
Extension: Replication of DNA occurs in vitro.
-
This cycle is repeated several times to generate up to one billion identical copies of DNA.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
From what you have learnt, can you tell whether enzymes are bigger or DNA is bigger in molecular size? How did you know?
Besides better aeration and mixing properties, what other advantages do stirred tank bioreactors have over shake flasks?
Describe briefly the following:
Downstream processing
Explain briefly:
PCR
A single strand of nucleic acid tagged with a radioactive molecule is called ______.
Significance of 'heat shock' method in bacterial transformation is to facilitate ______.
Which of the following steps are catalysed by Taq DNA polymerase in a PCR reaction?
While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
Illustrate the design of a bioreactor. Highlight the difference between a flask in your laboratory and a bioreactor which allows cells to grow in a continuous culture system.
Read the paragraph given below and answer and questions that follow:
| Enzyme Taq polymerase, is extracted from a eubacterial microorganism Thermus aquaticus from Yellowstone National Park in Montana, USA and isolated by Chien et al. (1976). Taq polymerase successfully replaced the DNA polymerase from E.coli that was being used in PCR earlier and this shift revolutionised the PCR technique. |
- Taq polymerase after its discovery replaced E.coli DNA polymerase in PCR technique. Explain giving reasons why was the need felt for the change?
- What is a primer and its importance in PCR?
- Write the importance of PCR as a diagnostic tool.
