Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Suggest and describe a technique to obtain multiple copies of a gene of interest in vitro.
उत्तर
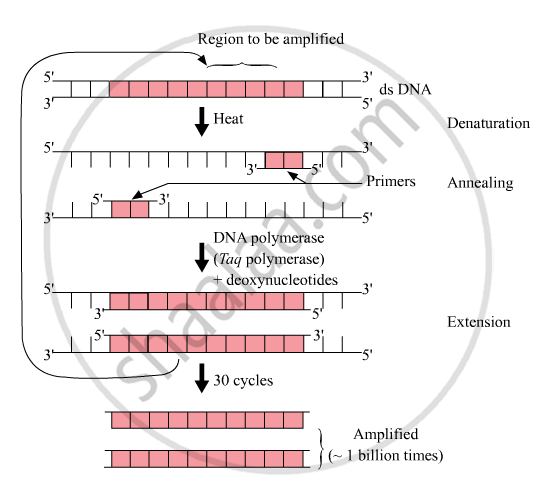
For the PCR, two sets of primers (chemically synthesised oligonucleotides that are complementary to a region of DNA), the enzyme DNA polymerase and deoxynucleotides are added.
The PCR consists of three steps:
-
Denaturation: Double helical DNA is denatured at a high temperature. DNA polymerase does not get degraded at this temperature, as the DNA polymerase used in this reaction is thermostable. It is isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus (Taq).
-
Annealing: It is the step in which primers are annealed to single-stranded DNA templates. Two sets of primers (chemically synthesised small oligonucleotides that are
complementary to the regions of DNA) are used. The temperature of the reaction mixture is lowered to 50–65 °C for some seconds to allow annealing of the primers. DNA polymerase extends the primer in the 5' to 3' direction. -
Extension: Replication of DNA occurs in vitro.
-
This cycle is repeated several times to generate up to one billion identical copies of DNA.
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
Explain briefly:
PCR
PCR proceeds mthree distinct steps governed by temperature, they are in order of ______.
In PCR, primers are used for ______.
During the process of gene amplification using PCR, if a very high temperature is not maintained in the beginning, then which of the following steps of PCR will be affected first?
Which of the following contributed in popularising the PCR (polymerase chain reactions) technique?
Significance of 'heat shock' method in bacterial transformation is to facilitate ______.
Which of the following steps are catalysed by Taq DNA polymerase in a PCR reaction?
While doing a PCR, ‘denaturation’ step is missed. What will be its effect on the process?
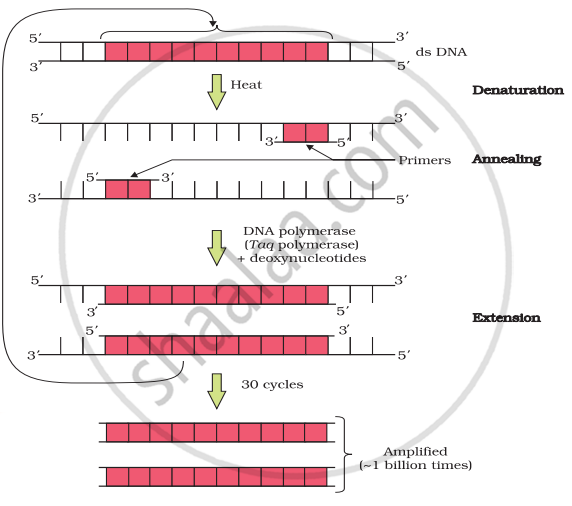
Identify and explain steps ‘A’, ‘B’ and ‘C’ in the PCR diagram given below.
Assertion (A): Synthetic oligonucleotide polymers are used during Annealing in a PCR.
Reason (R): The primers bind to the double stranded DNA at their complementary regions.
