Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Synthetic detergents have advantage over usual soaps as far as cleansing power is concerned. But use of synthetic detergents over a long time creates environmental pollution. How can the pollution caused by synthetic detergents be minimised? Classify the detergents according to their chemical nature.
Solution
Synthetic detergents are cleansing agents which have all the properties of soaps, but which actually do not contain any soap. These can be used both in soft and hard water as they given foam even in hard water. Detergents can be classified into three groups according their chemical nature.
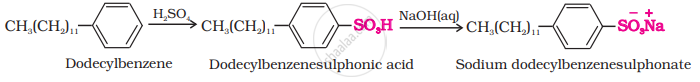
(i) Anionic Detergents: These are sodium salts of sulphonated long-chain alcohols or hydrocarbons. Alkyl hydrogen sulphates formed by treating long-chain alcohols with concentrated sulphuric acid are neutralised with alkali to form anionic detergents. Similarly alkyl benzene sulphonates are obtained by neutralising alkyl benzene sulphonic acids with alkali.
\[\ce{\underset{Lauryl alcohol}{CH3(CH2)10CH2OH} ->[H2SO4] \underset{Lauryl hydrogensulphate}{CH3(CH2)10CH2OSOH} ->[NaOH(aq)] \underset{(Anionic detergent)}{\underset{Sodium laurylsulphate}{CH3(CH2)10CH2OS\overset{_}{O}3\overset{+}{N}a}}}\]
In anionic detergents, the anionic part of the molecule is involved in the cleansing action.
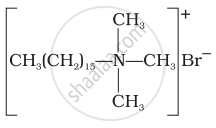
(ii) Cationic detergents: These are quaternary ammonium salts of amines with acetates, chlorides or bromides as anions.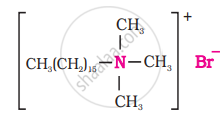
Cetyltrimethyl ammonium bromide
(iii) Non-ionic detergents: These do not contain any ion in their constitution, e.g., detergent formed by steric acid and polyethylene glycol.
\[\ce{\underset{Stearic acid}{CH3(CH2)16COOH} + \underset{Polyethleneglycol}{HO(CH2CH2O)nCH2CH2OH} ->[-H2O] CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O)nCH2CH2OH}\]
Pollution by synthetic detergents can be minimized by reducing the branching of hydrocarbon chain or using unbranched hydrocarbons.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are synthetic detergents better than soap?
Explain the following terms with suitable examples - Anionic detergents
Define the following term with a suitable example:
Cationic detergents
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Cationic detergents have germicidal properties.
(ii) Bacteria can degrade the detergents containing highly branched chains.
(iii) Some synthetic detergents can give foam even in ice cold water.
(iv) Synthetic detergents are not soaps.
Explain why some times foaming is seen in river water near the place where sewage water is poured after treatment?
Dishwashing soaps are synthetic detergents. What is their chemical nature?
Draw the diagram showing micelle formation by the following detergent.
\[\ce{CH3(CH2)10CH2OS\overset{-}{O}3\overset{+}{N}a}\]
Match structures given in Column I with the type of detergents given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) \[\ce{CH3(CH2)16COO(CH2CH2O) nCH2CH2OH}\] | (a) Cationic detergent |
| (ii) \[\ce{C17H35COO- Na+}\] | (b) Anionic detergent |
| (iii) \[\ce{CH3-(CH2)10CH2SO3- Na+}\] | (c) Nonionic detergent |
|
(iv) |
(d) Soap |
Define the following:
Cationic detergents
Explain the following terms with suitable examples Cationic detergents