Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Take 5 examples from your surroundings and give an explanation based on Newton's laws of motion.
Solution
- Example 1:
When we travel by bus, the stopped bus first feels backwards as it starts. This is an example of Newton's first law of motion.
Explanation:- When an object is at rest or in motion, the object does not change its state by its own inertia.
- When the bus is at rest, we are also at rest inside that bus.
- When the bus starts, sitting in the bus also gives us speed; But the upper part of the body tries to remain in a state of rest.
- As a result, inertia at rest tends to push us back. So, the bus starts in the next direction.
- Example 2:
When the carpet is lifted and shaken, the dust in it falls down. This is an example of Newton's first law of motion.
Explanation:
- When the carpet is lifted and cleaned, its speed increases.
- There is dust on the carpet and it is at rest due to inertia.
- Shaking removes the dust particles from the carpet, gravity causes the loose particles to fall, and the carpet is cleaned.
- Example 3:
Players withdraw their hands while catching the ball. This is an example of Newton's second law of motion.
Explanation:
- Players move their arms backwards to catch the ball, allowing more time for the hands to catch the ball.
- According to Newton's second law of motion, the change in momentum is proportional to the magnitude of the force.
- Taking more time to catch the ball results in a very small change in momentum. Therefore, the player catches the ball with less force and his hand is not jerked.
- Example 4:
The book placed on the table remains the same. This is an example of Newton's third law.
Explanation:
- A book placed on a table has some weight because this weight is the force exerted on the table.
- According to Newton's third law of motion, action and reaction forces act simultaneously.
- Hence, the force exerted on the book towards the table and the weight of the book balance.
- Also, the two forces are balanced, and there is no acceleration. Hence, the book placed on the table remains stationary.
- Example 5:
A balloon filled with air goes forward when released from the hand. This is an example of Newton's third law of motion.
Explanation:
As the air is released downward, it exerts an equal opposite force on the balloon, pushing the balloon forward.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
In real life, objects never travel with uniform velocity, even on a horizontal surface, unless something is done? Why is it so? What is to be done?
For the study of any kind of motion, we never use Newton’s first law of motion directly. Why should it be studied?
Answer the following question.
You are inside a closed capsule from where you are not able to see anything about the outside world. Suddenly you feel that you are pushed towards your right. Can you explain the possible cause (s)? Is it a feeling or a reality? Give at least one more situation like this.
Solve the following problem.
A truck of mass 5 ton is travelling on a horizontal road with 36 km hr-1, stops on traveling 1 km after its engine fails suddenly. What fraction of its weight is the frictional force exerted by the road? If we assume that the story repeats for a car of mass 1 ton i.e., car moving at the same speed stops at a similar distance, how much will the fraction be?
A batsman hits a ball of mass 0.2 kg straight towards the bowler without changing its initial speed of 6 m/s. What is the impulse imparted to the ball?
N number of balls of mass m kg moving along positive direction of X-axis, strike a wall per second and return elastically. The velocity of each ball is u m/s. The force exerted on the wall by the balls in newton, is ______.
Three blocks with masses m, 3m and 6m are connected by strings, as shown in the figure. After an upward force F is applied on block m, the masses move upward at constant speed v. What is the net force on the block of mass 3 m? (g is the acceleration due to gravity)
A particle moves in the x-y plane under the action of a force `vec"F"` such that the value of its linear momentum `(vec"p")` at any time t is Px = 2 cos t, py = 2 sin t. The angle `theta` between `vec"F"` and `vec"P"` at a given time twill be ____________.
A light string passing over a smooth light pulley connects two block of masses m1 and m2 (vertically). If the acceleration of the system is (3g/7), then the ratio of masses is ____________.
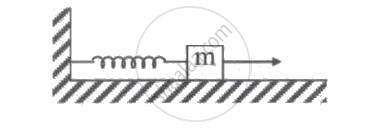
A block of mass m, lying on a smooth horizontal surface, is attached to a spring (of negligible mass) of spring constant k. The other end of the spring is fixed, as shown in the figure. The block is initially at rest in its equilibrium position. If now the block is pulled with a constant force F, the maximum speed of the block is: ____________.
A ball kept at 20 m height falls freely in downward direction vertically and hits the ground. The coefficient of restitution is 0.4. After the first rebound, the upward velocity is g = 10 m/s2 ?
A nucleus of rest splits into two nuclear parts having radii in the ratio 1 : 2. Their velocities are in the ratio.
