Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The incident rays and refracting rays are on opposite sides of the normal.
Options
Right
Wrong
Solution
The incident rays and refracting rays are on opposite sides of the normal- Right
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
| Column I | Column II | Column III | |
| 1 | Dispersion | Long-sightedness | Twinkling of stars |
| 2 | Refraction | Splitting of white light into component colours | Convex lens |
| 3 | Hypermetropia | Change in the direction of the ray of light due to change in medium | Spectrum of seven colours |
Fill in the following blank with a suitable word:
When light is reflected, the angles of incidence and reflection are ............ .
A ray of light strikes a plane mirror such that its angle of incidence is 30°. What angle does the reflected ray make with the mirror surface?
The letter F is placed in front of a plane mirror:
How would its image look like when seen in a plane mirror?
What is the difference between regular reflection of light and diffuse reflection of light?
Define the following terms used in the study of reflection of light by drawing a labelled ray-diagram:
(a) Incident ray
(b) Point of incidence
(c) Normal
(d) Reflected ray
(e) Angle of incidence
(f) Angle of reflection
State and explain the laws of reflection of light at a plane surface (like a plane mirror), With the help of a labelled ray-diagram. Mark the angles of 'incidence' and 'reflection' clearly on the diagram. If the angle of reflection is 47.5°, what will be the angle of incidence?
If a ray of light goes form a denser medium to a rarer medium, will it bend towards the normal or away from the normal?
In which material do you think light rays travel faster-glass or air?
A ray of light travelling in air is incident on a rectangular glass block and emerges out into the air from the opposite face. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the completer path of this ray of light. Mark the two points where the refraction of light takes place. What can you say about the final direction of ray of light?
With the help of a labelled diagram, explain why a tank full of water appears less deep than it actually is.
Show the lateral displacement of the ray on the diagram.
A ray of light when passes from glass to air, bends towards the normal.
What do you understand by refraction of light?
Draw suitable diagrams to illustrate how a beam of light incident parallel to the principal axis is reflected by:
(a) a concave mirror, and (b) a convex mirror
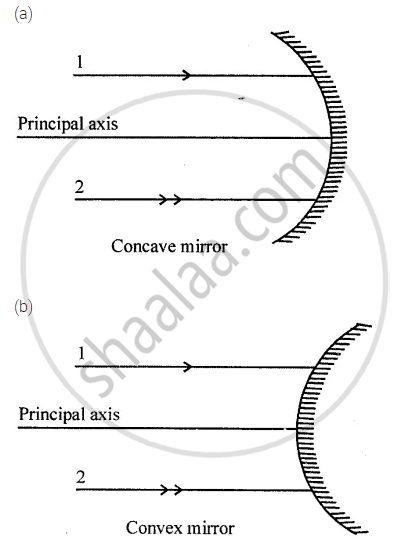
The diagram (figure) given below shows two parallel rays 1 and 2 incident on (a) a concave mirror, (b) a convex mirror. Draw the reflected rays and mark the focus by the symbol F.
A ray of light passes from medium 1 to medium 2. Which of the following quantities of the refracted ray will differ from that of the incident ray: Speed, intensity, frequency, wavelength?
Choose and write the correct option.
If we gradually increase the angle of incidence of a ray of light passing through prism then …..
Define the principal focus of a concave mirror.
What is atmospheric reflection? Explain with the help of a labelled diagram that the position of a star as seen by us is not its true position.
List four characteristics of the image formed by a concave lens of focal length 20 cm when the object is placed at a distance of 40 cm from its optical centre.
List in proper sequence the steps of the experiment for determining the approximate focal length of a given concave mirror by obtaining the image of a distant object.
Due to _______ pencil looks bent in water, in the given experiment.

Write scientific reason.
The sun appears on the western horizon for some time after sunset.
Explain the working of a periscope.
The deviation of light ray from its path when it travels from one transparent medium to another transparent medium is called ______.
If a beam of red light and a beam of violet light are incident at the same angle on the inclined surface of a prism from air medium and produce angles of refraction r and v respectively, which of the following is correct?

The angle of incidence from air to glass at the point O on the hemispherical glass slab is.
Light bends as it passes from one medium to another. What is this phenomenon called?
A ray of light traveling in medium 1 strikes and travels into another transparent medium 2. If the speed of light is greater in medium 1, the ray will ______.
The ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of ______ is constant.
Mirage is an example of refraction and the total internal reflection of light.
In refraction of light through a glass slab, the directions of the incident ray and the refracted ray are ______.
A ray of light starting from diamond is incident on the interface separating diamond and water. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show. the refraction of light in this case.
