Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The initial velocity of a car is 10 ms-1. It moves with an acceleration of 2 ms-2. What will be its speed after 10 seconds?
Solution
Initial velocity u =10 ms-1.
Acceleration a = 2 ms-2.
Time t = 10 s.
By using first equation of motion
V = u + at.
V = 10 + 2 X 10.
V (final velocity) = 30 ms-1.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State the type of motion represented by the following sketches in Figures.
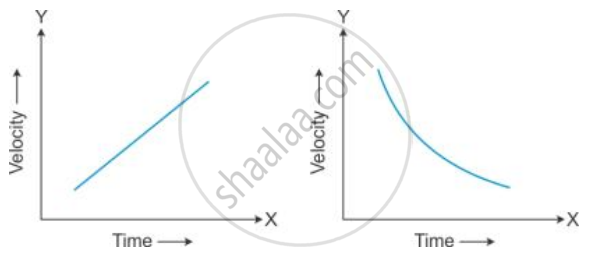
Give an example of each type of motion.
Figure given below shows a velocity-time graph for a car starting from rest. The graph has three parts AB, BC and CD.
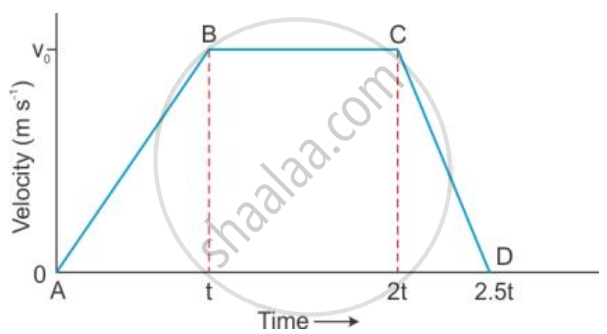
(a) Is the magnitude of acceleration higher or lower than that of retardation ? Give a reason .
(b) Compare the magnitude of acceleration and retardation .
A car travels with uniform velocity of 25 m s-1 for 5 s. The brakes are then applied and the car is uniformly retarded and comes to rest in further 10 s. Find:
- The distance which the car travels before the brakes are applied,
- Retardation and
- The distance travelled by car after applying the brakes.
Draw velocity – time graph for the following situation:
When a body is moving with variable velocity, but uniform retardation.
Is it possible for an accelerating body to have constant speed?
Convert the following acceleration:
1/36 m/s2 into km/h2
A bus accelerating with 4ms-2 changes its speed from 60ms_1 to a certain value in 5s. The final speed is ______.
Acceleration is defined as the rate of change of ______.
If a body starts from rest, what can be said about the acceleration of the body?
Assertion: Position-time graph of a stationary object is a straight line parallel to the time axis.
Reason: For a stationary object, the position does not change with time.
