Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Solution
Let final temp. of mixture = T°C
∴ Rise in temp. of cold water = T - t = 15°C
Let C be the Specific heat capacity of water
Heat lost by hot water = Heat gained by cold water
Mass × C × fall in temperature = Mass × C × Rise in temperature
⇒ 300 × C × (50 - T) = 600 × C × (T - t)
⇒ 50 - T = 2 × [15]
⇒ T = 50 - 30 = 20
But rise in temperature = T - initial temperature of cold water
⇒ 15 = 20 - t
∴ t = 20 - 15 = 5°C
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Name the law on which the principle of mixtures is based
(a) Calculate the heat capacity of a copper vessel of mass 150g if the specific heat capacity of copper is `410 J kg^-1 K^-1`
(b) How much heat energy will be required to increase the temperature of the vessel in part (a) from 25°C to 35°C?
Calculate the amount of heat energy required to raise the temperature of 100 g of copper from 20°C to 70°C. specific heat capacity of copper = `390 J kg^-1 K^-1`.
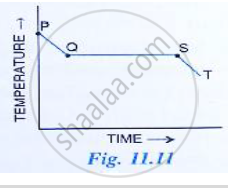
Fig 11. 11 shows the variation in temperature with time when some wax cools from the liquid phase to the solid phase.
(i) In which part of the curve, the wax is in liquid phase?
(ii) What does the part QS of the curve represent?
(iii) In which part of the curve, the wax will be the in the liquid as well as solid phase?
(iv) In which part of the curve, the wax is in solid phase?
(i) Define Calorimetry.
(ii) Name the material used for making a Calorimeter.
(iii) Why is a Calorimeter made up of thin sheets of the above material answered in (ii).
Which requires more heat: 1 g ice at 0°C or 1 g water at 0°C to raise its temperature to 10°C? Explain your answer.
State two impacts of global warming on the life on earth.
Name the material used for making a Calorimeter.
