Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The value of G varies from place to place.
Options
Right
Wrong
Solution
This statement is Wrong.
Explanation:
The value of a gravitational constant (G) is always the same irrespective of place. However, according to Newton's law of universal gravitation, the acceleration of gravity (g) varies with mass and the distance from its centre.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The value of G on the moon is about one-sixth `(1/6)`of the value of G on the earth.
Is the acceleration due to gravity of earth ‘g’ a constant ? Discuss.
An object takes 5 s to reach the ground from a height of 5 m on a planet. What is the value of g on the planet?
The value of gravitational acceleration (g) is ________ at the equator.
The mass of the moon is `1/81` of the mass of the earth. Its diameter is `1/3.7` of that of the earth. If acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the earth is 9.8 m/s2, then the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon.
When the value of acceleration due to gravity 'g' becomes `(g/3)` above the earth's surface at height 'h' then relation between 'h' and 'R' is ______.
R =radius of the earth
At a height R above the earth's surface, the gravitational acceleration is ______.
(R = radius of earth, g = acceleration due to gravity on earth's surface.)
The radius of the orbit of a geostationary satellite is (mean radius of the earth R, angular velocity about an axis in ω and acceleration due to gravity on earth's surface is (g) ______.
In the relation F = `"G M" "m"//"d"^2`, the quantity G
The force of attraction between two unit point masses separated by a unit distance is called
Suppose the gravity of the earth suddenly becomes zero, then in which direction will the moon begin to move if no other celestial body affects it?
How does the force of attraction between the two bodies depend upon their masses and the distance between them? A student thought that two bricks tied together would fall faster than a single one under the action of gravity. Do you agree with his hypothesis or not? Comment.
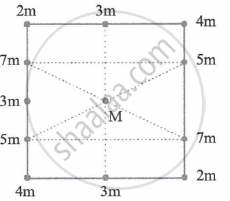
A central particle M is surrounded by a square array of other particles, separated by either distanced or distance d/2 along the perimeter o the square. The magnitude of the gravitational force on the central particle due to the other particles is ______.
A lift of mass 'm' is connected to a rope which is moving upward with maximum acceleration 'a'. For maximum safe stress, the elastic limit of the rope is 'T'. The minimum diameter of the rope is ______.
(g = gravitational acceleration)
The depth 'd' at which the value of acceleration due to gravity becomes `"I"/"n"` times the value at the earth's surface is ______. (R = radius of earth)
The value of gravitational acceleration g at a height h above the earth's surface is `"g"/4`, then ______. (R = radius of earth)
The acceleration due to gravity on the earth of radius Re is ge, and that on moon of radius Rm, is gm. The ratio of the masses of the earth and moon is given by ______.
A uniform ring of mass M and radius r is placed directly above a uniform sphere of mass 8M and of same radius R. The centre of the ring is at a distance of d = `sqrt3`R from the centre of the sphere. The gravitational attraction between the sphere and the ring is ______.
