Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
In the relation F = `"G M" "m"//"d"^2`, the quantity G
Options
depends on the value of g at the place of observation
is used only when the earth is one of the two masses
is greatest at the surface of the earth
is the universal constant of nature
Solution
is the universal constant of nature
Explanation:
In the relation F = `"G" "Mm"/"d"^2` the quantity G is the universal constant of nature.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the value of g suddenly becomes twice its value, it will become two times more difficult to pull a heavy object along the floor. Why?
The radius of planet A is half the radius of planet B. If the mass of A is MA, what must be the mass of B so that the value of g on B is half that of its value on A?
The value of G varies from place to place.
Write scientific reason.
The value of g at the centre of the earth is zero.
The ratio of masses of two planets is 2:3 and the ratio of their radii is 4:7 Find the ratio of their accelerations due to gravity.
On the earth, a stone is thrown from a height in a direction parallel to the earth’s surface while another stone is simultaneously dropped from the same height. Which stone would reach the ground first and why?
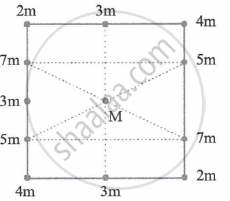
A central particle M is surrounded by a square array of other particles, separated by either distanced or distance d/2 along the perimeter o the square. The magnitude of the gravitational force on the central particle due to the other particles is ______.
A mass attached to one end of a string crosses top-most point on a vertical circle with critical speed. Its centripetal acceleration when string becomes horizontal will be ______. (g = gravitational acceleration)
A body is thrown from the surface of the earth with velocity 'u' m/s. The maximum height in m above the surface of the earth upto which it will reach is ______.
(R = radius of earth, g = acceleration due to gravity)
The value of gravitational acceleration g at a height h above the earth's surface is `"g"/4`, then ______. (R = radius of earth)
