Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Write scientific reason.
The value of g at the centre of the earth is zero.
Solution
- The acceleration due to gravity (g) on earth’s surface is given as, g = `"GM"/"R"^2`. The value of g depends on the mass M of the earth and the radius R of the earth.
- As we go inside the earth, our distance from the centre of the earth decreases and no longer remains equal to the radius of the earth (R).
- Along-with the distance, the part of the earth which contributes towards the gravitational force felt also decreases, decreasing the value of (M).
- Due to combined result of change in R and M, value of g becomes zero at the centre of the earth.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
State whether the following statement is true or false :
The value of G on the moon is about one-sixth `(1/6)`of the value of G on the earth.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The value of g on the earth is about………………. of that on the moon.
Explain why the value of g is zero at the centre of the earth.
The radius of planet A is half the radius of planet B. If the mass of A is MA, what must be the mass of B so that the value of g on B is half that of its value on A?
The CGS unit of G is dyne.cm2/g2.
Write scientific reason.
The weight of an object varies on different planets.
______ is used to change the speed of the car.
The mass of a body on the surface of the earth is 10 kg. The mass of the same body on the surface on the moon is `"g"_"m" = 1/6 "g"_"e"`, where gm, ge acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the moon and the earth respectively.
The depth 'd' below the surface of the earth at which acceleration due to gravity becomes `(g/n)` is ______.
R = radius of the earth, 'g' = acceleration due to gravity, n = integer
A wire AB is carrying steady current 'I1' and is kept on the table. Another wire CD carrying current 'I2' is held parallel and directly above AB at a distance 'r'. When wire CD is left free and it remains suspended at its position, its mass per unit length is (g =acceleration due to gravity) ____________.
The radius of the orbit of a geostationary satellite is (mean radius of the earth R, angular velocity about an axis in ω and acceleration due to gravity on earth's surface is (g) ______.
On the earth, a stone is thrown from a height in a direction parallel to the earth’s surface while another stone is simultaneously dropped from the same height. Which stone would reach the ground first and why?
Suppose the gravity of the earth suddenly becomes zero, then in which direction will the moon begin to move if no other celestial body affects it?
How does the force of attraction between the two bodies depend upon their masses and the distance between them? A student thought that two bricks tied together would fall faster than a single one under the action of gravity. Do you agree with his hypothesis or not? Comment.
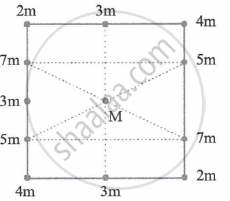
A central particle M is surrounded by a square array of other particles, separated by either distanced or distance d/2 along the perimeter o the square. The magnitude of the gravitational force on the central particle due to the other particles is ______.
The moon has a mass of 1/81 that of the earth and a radius of 1/4 that of the earth. The escape speed from the surface of the earth is 11.2 km/s. The escape speed from the surface of the moon is ______.
The value of gravitational acceleration g at a height h above the earth's surface is `"g"/4`, then ______. (R = radius of earth)
The acceleration due to gravity on the earth of radius Re is ge, and that on moon of radius Rm, is gm. The ratio of the masses of the earth and moon is given by ______.
