Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The work done by all the forces (external and internal) on a system equals the change in ______.
Options
total energy
kinetic energy
potential energy
none of these
Solution
The work done by all the forces (external and internal) on a system equals the change in kinetic energy.
Explanation:
As we know that the work done by the external force changes into the total energy but the internal force acting in the object can only vibrate the molecules or the atoms which further leads to the movement as the result of which Kinetic energy also increases.
Thus, the work done by all the forces (External or Internal) will completely lead to increases in the kinetic energy.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A lawyer alleges in court that the police had forced his client to issue a statement of confession. What kind of force is this ?
Is it true that the reaction of a gravitational force is always gravitational, of an electromagnetic force is always electromagnetic and so on?
List all the forces acting on (a) the pulley A, (b) the boy and (c) the block C in figure.
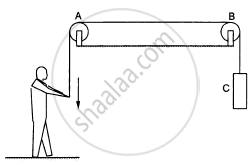
Figure shows a boy pulling a wagon on a road. List as many forces as you can which are relevant with this figure. Find the pairs of forces connected by Newton's third law of motion.
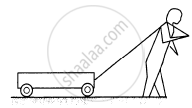
Figure shows a cart. Complete the table shown below.
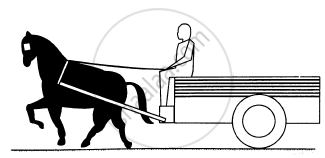
| Force on | Force by | Nature of the Force | Direction |
| Cart |
1 |
||
| Horse |
1 |
||
| Driver |
1 |
If all matters were made of electrically neutral particles such as neutrons,
(a) there would be no force of friction
(b) there would be no tension in the string
(c) it would not be possible to sit on a chair
(d) the earth could not move around the sun.
Which of the following systems may be adequately described by classical physics ?
(a) motion of a cricket ball
(b) motion of a dust particle
(c) a hydrogen atom
(d) a neutron changing to a proton.
Find the ratio of the magnitude of the electric force to the gravitational force acting between two protons.
The average separation between the proton and the electron in a hydrogen atom in ground state is 5.3 × 10−11 m. (a) Calculate the Coulomb force between them at this separation. (b) When the atom goes into its first excited state the average separation between the proton and the electron increases to four times its value in the ground state. What is the Coulomb force in this state?
In tug of war, the team that exerts a larger tangential force on the ground wins. Consider the period in which a team is dragging the opposite team by applying a larger tangential force on the ground. List which of the following works are positive, which are negative and which are zero?
(a) work by the winning team on the losing team
(b) work by the losing team on the winning team
(c) work by the ground on the winning team
(d) work by the ground on the losing team
(e) total external work on the two teams.
The magnetic force on a charged particle is always perpendicular to its velocity. Can the magnetic force change the velocity of the particles? Speed of the particle?
A box is pushed through 4.0 m across a floor offering 100 N resistance. How much work is done by the resisting force?
A particle moves from a point \[\overrightarrow{r}_1 = \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] to another point
\[\overrightarrow{r}_2 = \left( 3 m \right) \overrightarrow{ i } + \left( 2 m \right) \overrightarrow{ j } \] acts on it. Find the work done by the force on the particle during the displacement.
Find the average frictional force needed to stop a car weighing 500 kg at a distance of 25 m if the initial speed is 72 km/h.
Find the average force needed to accelerate a car weighing 500 kg from rest to 72 km/h through a distance of 25 m.
A block of mass 2.0 kg is pushed down an inclined plane of inclination 37° with a force of 20 N acting parallel to the incline. It is found that the block moves on the incline with an acceleration of 10 m/s2. If the block started from rest, find the work done (a) by the applied force in the first second, (b) by the weight of the block in the first second and (c) by the frictional force acting on the block in the first second. Take g = 10 m/s2.
The 200 m free-style women's swimming gold medal at Seoul Olympics in 1988 was won by Heike Friendrich of East Germany when she set a new Olympic record of 1 minute and 57⋅56 seconds. Assume that she covered most of the distance with a uniform speed and had to exert 460 W to maintain her speed. Calculate the average force of resistance offered by the water during the swim.
A block of mass 1 kg is placed at point A of a rough track shown in figure following. If slightly pushed towards right, it stops at point B of the track. Calculate the work done by the frictional force on the block during its transit from A to B.

A body is being raised to a height h from the surface of earth. What is the sign of work done by gravitational force?
