Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
The Young’s modulus for steel is much more than that for rubber. For the same longitudinal strain, which one will have greater tensile stress?
Solution
Here `Y = "stress"/"strain"`
According to question, longitudinal stress for rubber and steel are equal
So, `Y ∝ Stress`
`Y_(Steel)/Y_(Rub ber) = (Stress)_(Steel)/(Stress)_(Rub ber)`
∵ `Y_(Steel) > Y_(Rub ber)`
`Y_(Steel)/Y_A > 1`
`(Stress)_(Steel) > (Stress)_(Rub ber)`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A wire elongates by 1.0 mm when a load W is hung from it. If this wire goes over a a pulley and two weights W each are hung at the two ends, he elongation of he wire will be
A student plots a graph from his reading on the determination of Young modulus of a metal wire but forgets to put the labels. the quantities on X and Y-axes may be respectively
(a) weight hung and length increased
(b) stress applied and length increased
(c) stress applied and strain developed
(d) length increased and the weight hung.
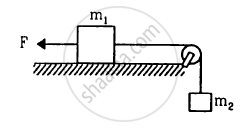
Consider the situation shown in figure. The force F is equal to the m2 g/2. If the area of cross section of the string is A and its Young modulus Y, find the strain developed in it. The string is light and there is no friction anywhere.
The temperature of a wire is doubled. The Young’s modulus of elasticity ______.
Identical springs of steel and copper are equally stretched. On which, more work will have to be done?
In nature, the failure of structural members usually result from large torque because of twisting or bending rather than due to tensile or compressive strains. This process of structural breakdown is called buckling and in cases of tall cylindrical structures like trees, the torque is caused by its own weight bending the structure. Thus the vertical through the centre of gravity does not fall within the base. The elastic torque caused because of this bending about the central axis of the tree is given by `(Ypir^4)/(4R) . Y` is the Young’s modulus, r is the radius of the trunk and R is the radius of curvature of the bent surface along the height of the tree containing the centre of gravity (the neutral surface). Estimate the critical height of a tree for a given radius of the trunk.
If Y, K and η are the values of Young's modulus, bulk modulus and modulus of rigidity of any material respectively. Choose the correct relation for these parameters.
A metal wire of length L, area of cross section A and Young's modulus Y behaves as a spring of spring constant k given by:
A boy's catapult is made of rubber cord which is 42 cm long, with a 6 mm diameter of cross-section and negligible mass. The boy keeps a stone weighing 0.02 kg on it and stretches the cord by 20 cm by applying a constant force. When released, the stone flies off with a velocity of 20 ms-1. Neglect the change in the area of the cross-section of the cord while stretched. Young's modulus of rubber is closest to ______.
The force required to stretch a wire of cross section 1 cm2 to double its length will be ______.
(Given Young's modulus of the wire = 2 × 1011 N/m2)
