Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
A student plots a graph from his reading on the determination of Young modulus of a metal wire but forgets to put the labels. the quantities on X and Y-axes may be respectively
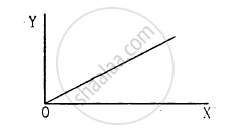
(a) weight hung and length increased
(b) stress applied and length increased
(c) stress applied and strain developed
(d) length increased and the weight hung.
Solution
All options are correct.
(a) When a weight is loaded on a wire, the length of the wire increases. The relationship between weight and length is linear.
(b) When a weight is loaded, it produces stress on the wire. The relationship between stress and increase in length is also linear.
(c) When stress is applied, strain develops. Therefore, both are linearly related.
(d) Since the value of Y for the wire is unknown, X may also be the increase in its length. Nevertheless, they still show the same linear relationship.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A steel wire of length 4.7 m and cross-sectional area 3.0 × 10–5 m2 stretches by the same amount as a copper wire of length 3.5 m and cross-sectional area of 4.0 × 10–5 m2 under a given load. What is the ratio of Young’s modulus of steel to that of copper?
Two wires of diameter 0.25 cm, one made of steel and the other made of brass are loaded as shown in Fig. 9.13. The unloaded length of steel wire is 1.5 m and that of brass wire is 1.0 m. Compute the elongations of the steel and the brass wires.

A 14.5 kg mass, fastened to the end of a steel wire of unstretched length 1.0 m, is whirled in a vertical circle with an angular velocity of 2 rev/s at the bottom of the circle. The cross-sectional area of the wire is 0.065 cm2. Calculate the elongation of the wire when the mass is at the lowest point of its path.
Two wires A and B are made of same material. The wire A has a length l and diameter rwhile the wire B has a length 2l and diameter r/2. If the two wires are stretched by the same force, the elongation in A divided by the elongation in B is
The length of a metal wire is l1 when the tension in it T1 and is l2 when the tension is T2. The natural length of the wire is
The temperature of a wire is doubled. The Young’s modulus of elasticity ______.
The Young’s modulus for steel is much more than that for rubber. For the same longitudinal strain, which one will have greater tensile stress?
Identical springs of steel and copper are equally stretched. On which, more work will have to be done?
If the yield strength of steel is 2.5 × 108 Nm–2, what is the maximum weight that can be hung at the lower end of the wire?
In nature, the failure of structural members usually result from large torque because of twisting or bending rather than due to tensile or compressive strains. This process of structural breakdown is called buckling and in cases of tall cylindrical structures like trees, the torque is caused by its own weight bending the structure. Thus the vertical through the centre of gravity does not fall within the base. The elastic torque caused because of this bending about the central axis of the tree is given by `(Ypir^4)/(4R) . Y` is the Young’s modulus, r is the radius of the trunk and R is the radius of curvature of the bent surface along the height of the tree containing the centre of gravity (the neutral surface). Estimate the critical height of a tree for a given radius of the trunk.
If Y, K and η are the values of Young's modulus, bulk modulus and modulus of rigidity of any material respectively. Choose the correct relation for these parameters.
A metal wire of length L, area of cross section A and Young's modulus Y behaves as a spring of spring constant k given by:
A uniform metal rod of 2 mm2 cross section is heated from 0°C to 20°C. The coefficient of linear expansion of the rod is 12 × 10-6/°C, it's Young's modulus is 1011 N/m2. The energy stored per unit volume of the rod is ______.
If the length of a wire is made double and the radius is halved of its respective values. Then, Young's modules of the material of the wire will ______.
