Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
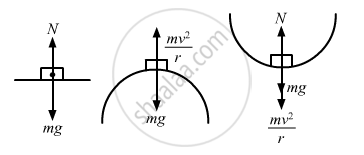
Three identical cars A, B and C are moving at the same speed on three bridges. The car A goes on a place bridge, B on a bridge convex upward and C goes on a bridge concave upward. Let FA, FB and FC be the normal forces exerted by the car on the bridges when they are at the middle of bridges.
Options
FA is maximum of the three forces.
FB is maximum of the three forces.
FC is maximum of the three forces.
FA = FB = FC.
Solution
FC is maximum of the three forces.
At the middle of bridge, normal force can be given as : \[\text{N}_\text{A} = \text{mg}\]
\[\text{N}_\text{B} = \frac{\text{mv}^2}{\text{r}} - \text{mg}\]
\[ \text{N}_\text{C} = \frac{\text{mv}^2}{\text{r}} + \text{mg}\]
So, FC is maximum.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A stone of mass 0.25 kg tied to the end of a string is whirled round in a circle of radius 1.5 m with a speed of 40 rev/min in a horizontal plane. What is the tension in the string? What is the maximum speed with which the stone can be whirled around if the string can withstand a maximum tension of 200 N?
A disc revolves with a speed of `33 1/3` rev/min, and has a radius of 15 cm. Two coins are placed at 4 cm and 14 cm away from the centre of the record. If the co-efficient of friction between the coins and the record is 0.15, which of the coins will revolve with the record?
A smooth block loosely fits in a circular tube placed on a horizontal surface. The block moves in a uniform circular motion along the tube. Which wall (inner or outer) will exert a nonzero normal contact force on the block?
When a particle moves in a circle with a uniform speed
A car moves at a constant speed on a road as shown in figure. The normal force by the road on the car NA and NB when it is at the points A and B respectively.

A motorcycle is going on an overbridge of radius R. The driver maintains a constant speed. As the motorcycle is ascending on the overbridge, the normal force on it
If the earth stop rotating, the apparent value of g on its surface will
A scooter weighing 150 kg together with its rider moving at 36 km/hr is to take a turn of a radius 30 m. What horizontal force on the scooter is needed to make the turn possible ?
What is the radius of curvature of the parabola traced out by the projectile in the previous problem at a point where the particle velocity makes an angle θ/2 with the horizontal?
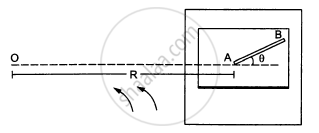
A table with smooth horizontal surface is fixed in a cabin that rotates with a uniform angular velocity ω in a circular path of radius R (In the following figure). A smooth groove AB of length L(<<R) is made the surface of the table. The groove makes an angle θ with the radius OA of the circle in which the cabin rotates. A small particle is kept at the point A in the groove and is released to move at the point A in the groove and is released to move along AB. Find the time taken by the particle to reach the point B.
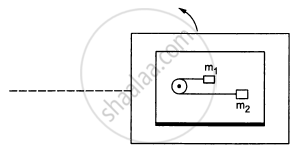
A table with smooth horizontal surface is placed in a circle of a large radius R (In the following figure). A smooth pulley of small radius is fastened to the table. Two masses m and 2m placed on the table are connected through a string going over the pulley. Initially the masses are held by a person with the string along the outward radius and then the system is released from rest (with respect to the cabin). Find the magnitude of the initial acceleration of the masses as seen from the cabin and the tension in the string.
A person stands on a spring balance at the equator. If the speed of earth's rotation is increased by such an amount that the balance reading is half the true weight, what will be the length of the day in this case?
A particle is moving in a radius R with constant speed v. The magnitude of average acceleration after half revolution is ____________.
A wheel is subjected to uniform angular acceleration about its axis. The wheel is starting from rest and it rotates through an angle θ1, in first two seconds. In the next two seconds, it rotates through an angle θ2. The ratio θ1/θ2 is ____________.
A child starts running from rest along a circular track of radius r with constant tangential acceleration a. After time the feels that slipping of shoes on the ground has started. The coefficient of friction between shoes and the ground is [g = acceleration due to gravity].
The real force 'F' acting on a particle of mass ' m' performing circular motion acts along the radius of circle 'r' and is directed towards the centre of circle. The square root of the magnitude of such force is (T = periodic time).
An engine requires 5 seconds to go from a speed of 600 r.p.m. to 1200 r.p.m. How many revolutions does it make in this period?
A stone tide to a string of length L is whirled in a vertical circle with the other end of the string at the centre. At a certain instant of time, the stone is at its lowest position and has a speed u. The magnitude of change in its velocity, as it reaches a position where the string is horizontal, is `sqrt(x("u"^2 - "gL")`. The value of x is ______.
