Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Two independent monohybrid crosses were carried out involving a tall pea plant with a dwarf pea plant. In the first cross, the offspring population has equal number of tall and dwarf plants, whereas in the second cross it was different. Work out the crosses and explain giving reasons for the difference in the offspring population.
Solution
A monohybrid cross is a cross where two forms of a single trait are hybridised. Mendel crossed pure tall pea plant with a pure dwarf pea plant and obtained all tall plants in the first filial generation. The character which appeared in the F1 generation is called dominant character, whereas the character which is not expressed in the F1 generation is called recessive. After inter-crossing the hybrids of the F1 generation, he obtained tall and dwarf progeny in the ratio 3:1 (phenotypic ratio), but the genetic ratio was 1:2:1 which is TT, Tt and tt.
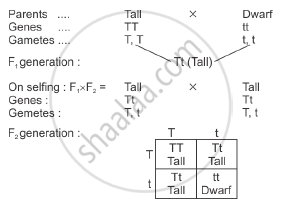
Such a cross depicts the law of dominance in which all traits are controlled by a pair of factors called genes. In a dissimilar pair of factors, one member of the pair is dominant, while the other is recessive.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why is human ABO blood group gene considered a good example of multiple alleles?
What is the inheritance pattern observed in the size of starch grains and seed shape of Pisum sativum? Workout the monohybrid cross showing the above traits. How does this pattern of inheritance deviate from that of Mendelian law of dominance?
In Snapdragon, a cross between true-breeding red flowered (RR) plants and truebreeding white flowered (rr) plants showed a progeny of plants with all pink flowers.
The appearance of pink flowers is not known as blending. Why?
A pleiotropic gene ______.
In Antirrhinum, RR is phenotypically red flowers, rr is white and Rr is pink. Select the correct phenotypic ratio in F1 generation when a cross is performed between RR X Rr: ______
The gene that controls the ABO blood group system in human beings has three alleles -IA, IB, and i. A child has blood group O. His father has blood group A and mother has blood group B. Genotypes of other offsprings can be: ______
- IB IB
- IA i
- IB i
- IA IB
- ii
Human with ______ blood group is considered as Universal Donor.
In blood:
A phenomenon in which neither of the alleles of a gene is completely dominant over the other and a hybrid is intermediate between the two parents is called ______
Four triplet codons code for the amino acid valine. Three of them are given below.
GUU GUC GUA
Write the fourth codon.
