Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Using Gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the distance from it.
Solution
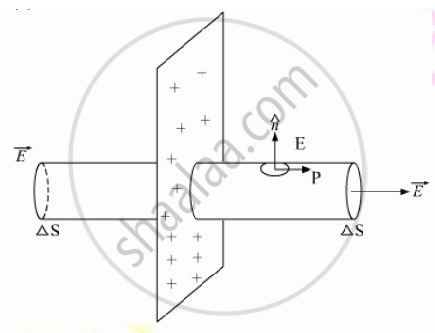
Consider a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet of charge density σ.
We have to find electric field E at point as shown in figure.
Now, we construct a Gaussian surface as shown in figure in the form of cylinder.
Applying Gauss’s Law,
`phi =oint vecE*dvecs =(σΔs)/in_0`
`=> E Deltas + EDelta +0 = (sigma Deltas)/in_0`
`= 2EDeltas = (sigma Deltas)/(in_0)`
`=> E = sigma /(2in_0)`
It shows that electric field is uniform due to charged infinite plane sheet. Also, we can say that E is independent from distance from the sheet.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Find the electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged spherical shell at a point (i) outside the shell. Plot the graph of electric field with distance from the centre of the shell.
Using Gauss's law in electrostatics, deduce an expression for electric field intensity due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet. If another identical sheet is placed parallel to it, show that there is no electric field in the region between the two sheets ?
A small conducting sphere of radius 'r' carrying a charge +q is surrounded by a large concentric conducting shell of radius Ron which a charge +Q is placed. Using Gauss's law, derive the expressions for the electric field at a point 'x'
(i) between the sphere and the shell (r < x < R),
(ii) outside the spherical shell.
How is the field directed if (i) the sheet is positively charged, (ii) negatively charged?
A spherical shell made of plastic, contains a charge Q distributed uniformly over its surface. What is the electric field inside the shell? If the shell is hammered to deshape it, without altering the charge, will the field inside be changed? What happens if the shell is made of a metal?
A rubber balloon is given a charge Q distributed uniformly over its surface. Is the field inside the balloon zero everywhere if the balloon does not have a spherical surface?
A positive point charge Q is brought near an isolated metal cube.
A spherical volume contains a uniformly distributed charge of density 2.0 × 10 -4 Cm-3 Find the electric field at a point inside the volume at a distance 4⋅0 cm from the centre.
A circular wire-loop of radius a carries a total charge Q distributed uniformly over its length. A small length dL of the wire is cut off. Find the electric field at the centre due to the remaining wire.
