Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Using Huygens's construction of secondary wavelets explain how a diffraction pattern is obtained on a screen due to a narrow slit on which a monochromatic beam of light is incident normally.
Solution
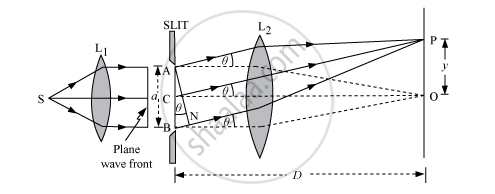
Consider a parallel beam of light from a lens falling on a slit AB. As diffraction occurs, the pattern is focused on the screen with the help of lens L2. We will obtain a diffraction pattern that is a central maximum at the centre O, flanked by a number of dark and bright fringes called secondary maxima and minima.
Each point on the plane wave front AB sends out secondary wavelets in all directions. The waves from points equidistant from the centre C, lying on the upper and lower half, reach point O with zero path difference and, hence, reinforce each other producing maximum intensity at point O.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
On the basis of Huygens' wave theory of light prove that velocity of light in a rarer medium is greater than velocity of light in a denser medium.
You have learnt in the text how Huygens’ principle leads to the laws of reflection and refraction. Use the same principle to deduce directly that a point object placed in front of a plane mirror produces a virtual image whose distance from the mirror is equal to the object distance from the mirror.
State Huygen's principle.
Use Huygens' principle to verify the laws of refraction.
The refractive indices of water and diamond are `4/3` and 2.42 respectively. Find the speed of light in water and diamond. (c = 3x108 m/s)
Use Huygens’s principle to explain the formation of diffraction pattern due to a single slit illuminated by a monochromatic source of light.
Huygens' principle of secondary wavelets may be used to
(a) find the velocity of light in vacuum
(b) explain the particle behaviour of light
(c) find the new position of a wavefront
(d) explain Snell's Law
For light diverging from a point source ______.
- the wavefront is spherical.
- the intensity decreases in proportion to the distance squared.
- the wavefront is parabolic.
- the intensity at the wavefront does not depend on the distance.
What type of wavefronts are associated with a point source of light?
Represent diagrammatically how the incident planar wavefronts of wavelength λ pass through an aperture of size d, when d is approximately equal to λ.
