Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What are the cells involved innate immune system?
Solution
Cells involved in innate immunity are monocytes (macrophages), neutrophils, helper T-cells, B-cells, dendritic cells.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Differentiate between
Active and passive immunity
Which blood cells secrete antibodies?
Crypts of lieberkuhn are present in ______.
If you suspect a major deficiency of antibodies in person, to which of the following would you look for confirmations evidence?
To which type of barriers under innate immunity, do the saliva in the mouth and the teal from the eyes, belong?
The yellowish fluid "colostrum" secreted by the mammary glands of the mother during the initial days of lactation has abundant antibodies (lgA) to protect the infant. This type of immunity is called:
Active immunity development is related to ______.
Transplantation of tissues/organs to save certain patients often fails due to rejection of such tissues/organs by the patient. Which type of immune response is responsible for such rejections?
Why is mother's milk considered the most appropriate food for a new born infant?
Why is an antibody molecule represented as H2L2?
Differentiate between active immunity and passive immunity.
For an organ transplant, it is an advantage to have an identical twin. Why?
Cellular factors in innate immunity is provided by ______.
Apis mellifera are killer bees possessing toxic bee venom. Identify the treatment and the type of immunity developed from the given table to treat a person against the venom of this bee.
The decrease in the T-lymphocyte count in human blood will result in ______.
| When a microorganism invades a host, a definite sequence of events usually occurs leading to infection and disease, causing suffering to the host. This process is called pathogenesis. Once a microorganism overcomes the defence system of the host, development of the disease follows a certain sequence of events as shown in the graph. Study the graph given below for the sequence of events leading to the appearance of a disease and answer the questions that follow: |
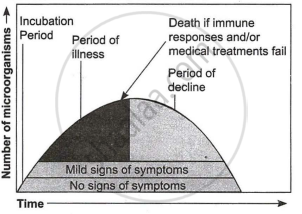
(a) In which period, according to the graph there are maximum chances of a person transmitting a disease/infection and why? (1)
(b) Study the graph and write what is an incubation period. Name a sexually transmitted disease that can be easily transmitted during this period. Name the specific type of lymphocytes that are attacked by the pathogen of this disease. (2)
OR
(b) Draw a schematic labelled diagram of an antibody. (2)
(c) In which period, the number of immune cells forming antibodies will be the highest in a person suffering from pneumonia? Name the immune cells that produce antibodies. (1)
Interferons are proteins. In humans they are secreted by ______.
Tetanus antitoxin (Tetanus toxoid) when injected into the human body it immediately provides ______.
A patient was given an anti-retroviral drug by the doctor.
Which disease was the patient diagnosed with?
The following is well-known abbreviation, which have been used in this chapter. Expand to its full form:
CMI
