Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What do you understand by the term "electric potential"? (or potential) at a point? What is the unit of electric potential?
Solution
The electric potential (or potential) at a point in an electric field is defined as the work done in moving a unit positive charge from infinity to that point. It is denoted by the symbol, V and its unit is volt.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What is the SI unit of potential difference?
A potential difference of 20 volts is applied across the ends of a resistance of 5 ohms. What current will flow in the resistance?
Explain the analogy between the flow of charge (or current) in a conductor under a potential difference with the free fall of a body under gravity.
The following table shows current in Amperes and potential difference in Volts.
Which law will the graph prove? Explain the law.

The device used for measuring potential difference is
From the following observations taken while determining the resistance of a conductor, draw the current-voltage graph and calculate the resistance of conductor. Is the conductor ohmic?
| Ammeter reading I (in ampere) | Voltmeter reading V (in volt) |
| 0.2 | 0.4 |
| 0.3 | 0.6 |
| 0.5 | 1.0 |
| 0.8 | 1.6 |
| 1.5 | 3.0 |
The figure shows a circuit. When the circuit is switched on, the ammeter reads 0.5 A.
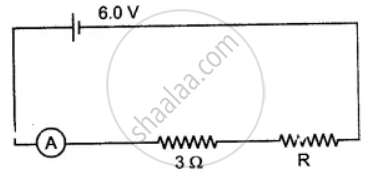
(i) Calculate the value of the unknown resistor R.
(ii) Calculate the charge passing through the 3 Ω resistor in 120 s.
(iii) Calculate the power dissipated in the 3 Ω resistor.
Conceptual question.
Does a solar cell always maintain the potential across its terminals constant? Discuss
A current of 1 ampere flows in a series circuit containing an electric lamp and a conductor of 5 Ω when connected to a 10 V battery. Calculate the resistance of the electric lamp.
Now if a resistance of 10 Ω is connected in parallel with this series combination, what change (if any) in current flowing through 5 Ω conductor and potential difference across the lamp will take place? Give reason.
Find out the following in the electric circuit given in Figure
- Effective resistance of two 8 Ω resistors in the combination
- Current flowing through 4 Ω resistor
- Potential difference across 4 Ω resistance
- Power dissipated in 4 Ω resistor
- Difference in ammeter readings, if any.

