Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is double fertilisation? Describe the process in brief.
Solution
Double fertilization is a major characteristic of flowering plants. In this process, two male gametes fuse with one female gamete wherein one male gamete fertilizes the egg to form a zygote, whereas the other fuses with two polar nuclei to form endosperm.
Double fertilization gives stimulus to the plant that results in the development of the ovary into fruit and ovules into seed. The fusion of haploid male and female gametes restores the diploid condition of the plant.
Process of double fertilisation:
- After successful pollination, the pollen grain germinates on the stigma to form the pollen tube.
- The pollen tube carries in the cytoplasm two male gametes and one tube nucleus into the ovary.
- The pollen tube enters the ovary mostly through the micropyle region, near the egg apparatus. This movement is guided by the filiform apparatus.
- Inside the ovary, the pollen tube absorbs water and bursts open, releasing the two male gametes and the tube nucleus.
- The tube nucleus degenerates, and the two male gametes prepare for fusion.
- One of the male gamete fuses with the egg cell to form the diploid zygote.
- The other male gamete fuses with the diploid secondary nucleus to form the primary endosperm nucleus (PEN).
- The zygote develops to form the new plant, while the PEN develops to form the endosperm, which provides nourishment to the developing embryo.

RELATED QUESTIONS
Where and how does triple fusion take place?
Read the following statement and answer the questions that follow :
"A guava fruit has 200 viable seeds."
(a) What are viable seeds?
(b) Write the total number of :
(i) Pollen grains (ii) Gametes
in producing 200 viable guava seeds.
c) Prepare a flow-chart to depict the post-pollination events leading to viable-seed production in a flowering plant.
Triple Fusion involves:
(i) Fusion of one male, gamete with female gamete
(ii) Fusion of tube nucleus with generative nvcleus
(iii) Fusion of two polar nuclei.
(iv) Fusion of second male gamete with two polar nuclei
Describe any two devices in a flowering plant which prevent both autogamy and geitonogamy.
During double fertilization second male gamete fuses with ___________.
Match the items in Column A with those in Column B.
|
Column A |
Column B |
|
(a) Generative nucleus |
(i) Pollen tube |
|
(b) Germ pore |
(ii) Endosperm nucleus |
|
(c) Exine |
(iii) Testa |
|
(d) Secondary nucleus |
(iv) Fertilization |
|
(e) Integument |
(v) Male nuclei |
|
(f) Egg nucleus |
(vi) Rough |
Given ahead is a diagrammatic sketch of the sectional view of a germinating pollen grain. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
What is the function of the part labelled '4'?
Given ahead is a diagrammatic representation of the process of fertilization. Study the same and then answer the question that follows:
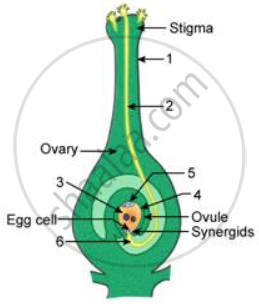
What happens to
i) Ovary
ii) Ovule after fertilisation
What is ‘double fertilization’? Describe it with the help of a neat and well-labeled diagram. Give its importance.
Explain the pollination process in maize.
Do you think fruits are important for the plant?
Long Answer Question:
Draw a labeled diagram of the L.S. of anatropous ovule and list the components of the embryo sac and mention their fate after fertilization.
Match the following
| I) | External fertilization | i) | pollen grain |
| II) | Androecium | ii) | anther wall |
|
III) |
Male gametophyte | iii) | algae |
| IV) | Primary parietal layer | iv) | stamens |
Explain the development of a Dicot embryo
Which of the following is the CORRECT sequence of events during double fertilization in Angiosperms?
In double fertilization, the first male gamete fuses with the egg and the second male gan1ete fuses with which of the following?
The success of seed plants on land is mainly due to ______.
By which of the following the megasporangium proper of an angiosperm ovule is represented?
Identify the function of filiform apparatus.
Through which route the pollen tube can enter the ovule?
The total number of nuclei involved in double fertilisation in angiospersm are ______.
In ______ sepal is seen on the fruit after fertilization.
Ovules fall off after fertilization.
Double fertilization is a distinctive feature of ______.
After fertilization, the seed coat of seeds develops from ______
In the diagram given below, show the path of a pollen tube from the pollen on the stigma into the embryo sac. Name the components of egg apparatus.
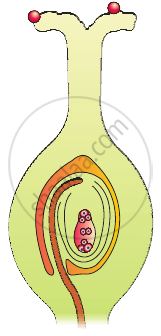
Which is the triploid tissue in a fertilised ovule? How is the triploid condition achieved?
What is the function of the two male gametes produced by each pollen grain in angiosperms?
What is Siphonogamy?
Give a term for the following:
Fusion of male gamete and secondary nucleus in angiosperms.
