Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What is nucleophiles? Give a suitable example.
Solution
Nucleophiles are reagents that has a high affinity for electropositive centers. They possess an atom that has an unshared pair of electrons. They are usually negatively charged ions or electron-rich neutral molecules.
Example:
NH3, R-NH2, R-SH, H2O, R-OH, CN–. OH– etc.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
For the following reactions
- \[\ce{CH3CH2CH2Br + KOH → CH3 – CH = CH2 + KBr + H2O}\]
- \[\ce{(CH3)3CBr + KOH → (CH3)3COH + KBr}\]
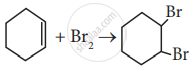
Which of the following statement is correct?
Decreasing order of nucleophilicity is ______.
Homolytic fission of covalent bond leads to the formation of ______.
Assertion: Tertiary Carbocations are generally formed more easily than primary Carbocations ions.
Reason: Hyper conjucation as well as inductive effect due to additional alkyl group stabilize tertiary carbonium ions.
The geometrical shape of carbocation is ______.
Write a short note on resonance.
Write a short note on hyperconjucation.
What is electrophiles? Give a suitable example.
Show the heterolysis of a covalent bond by using curved arrow notation and complete the following equation. Identify the nucelophile.
CH3 – Br + KOH →
Show the heterolysis of a covalent bond by using curved arrow notation and complete the following equation. Identify the nucelophile.
\[\ce{CH3 – O – CH3 + HI →}\]
