Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Which type or mirror is usually used as a rear-view mirror in motor cars?
Solution
A diverging mirror, i.e. convex mirror, is used as a rear-view mirror in motor cars, as it has a wider area of view, and always forms virtual, erect and small-sized images of a large number of objects at the same time.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Describe with a suitable diagram, how a convex mirror diverges a parallel beam of light rays. Mark clearly the pole, focus and centre of curvature of concave mirror in this diagram.
A mirror forms an image which is 30 cm from an object and twice its height.
(a) Where must the mirror be situated?
(b) What is the radius of curvature?
(c) Is the mirror convex or concave?
An object is kept at a distance of 5 cm in front of a convex mirror of focal length 10 cm. Calculate the position and magnification of the image and state its nature.
Draw ray diagrams to represent the nature, position and relative size of the image formed by a convex lens for the object placed:
between F1 and the optical centre O of the lens.
Which of the above two cases shows the use of convex lens as a magnifying glass? Give reasons for your choice.
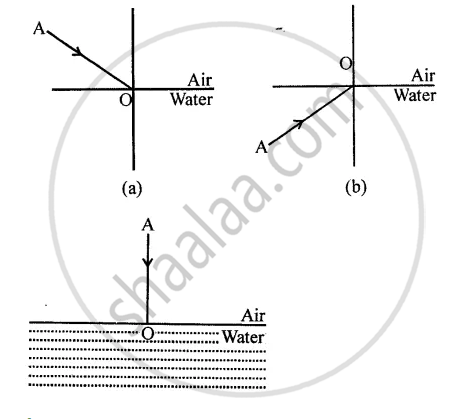
The diagram given below in fig shows a ray of light AO falling on a surface separating two media. Draw the refracted ray in each, case.
A 5 cm tall object is placed perpendicular to the principle axis of a convex lens of focal length 12 cm. The distance of the object from the lens is 8 cm. Using the lens formula, find the position, size and nature of the image formed.
Numerical problem.
A concave mirror produces three times magnified real image of an object placed at 7 cm in front of it. Where is the image located? (Ans: 21 cm in front of the mirror)
The nature of image formed by a convex mirror when the object distance from the mirror is less than the distance between pole and focal point (F) of the mirror would be ______.
Higher-Order Thinking Skills:
A convex mirror is in water. What should be the change in its focal length?
Match the following.
| Column I | Column II |
| Convex mirror | Radio telescopes |
| Parabolic mirror | Rear-view mirror |
| Snell’s law | Kaleidoscope |
| Dispersion of light | sin i/sin r =μ |
| Refractive index | Rainbow |
