Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Why does obtaining the image of the sun on paper with the help of a concave mirror burn the paper?
Solution
The rays from the Sun are parallel. When these rays fall on the concave mirror, they converge to a single point on the focal plane of the mirror. Thus a lot of heat is produced at that point. Now, if a paper is placed at that point to get the image of the Sun, the paper gets burnt because of the huge amount of heat concentrated at that point.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
It is desired to obtain an erect image of an object, using concave mirror of focal length of 12 cm.
Will the image be smaller or larger than the object? Draw ray diagram to show the formation of image in this case.
List four characteristics of the images formed by plane mirrors.
To construct ray diagrams, two rays of light are generally so chosen that it is easy to determine their directions after reflection from a mirror. Choose two such rays and state the path/direction of these rays after reflection from a concave mirror. Use these two rays to find the position and nature of the image of an object placed at a distance of 8 cm from a concave mirror of focal length 12 cm.
A spherical mirror produces an image of magnification −1 on a screen placed at a distance of 40 cm from the mirror:
(i) Write the type of mirror.
(ii) What is the nature of the image formed?
(iii) How far is the object located from the mirror?
(iv) Draw the ray diagram to show the image formation in this case.
To construct a ray diagram we use two rays which are so chosen that it is easy to know their directions after reflection from the mirror. List two such rays and state the path of these rays after reflection in case of concave mirrors. Use these two rays and draw ray diagram to locate the image of an object placed between pole and focus of a concave mirror.
The angle between an incident ray and the plane mirror is 30°. The total angle between the incident ray and reflected ray will be:
(a) 30°
(b) 60°
(c) 90°
(d) 120°
What is a spherical mirror? Distinguish between a concave mirror and a convex mirror.
With the help of a ray diagram, determine the position, nature and size of the image formed of an object placed at the centre of curvature of a concave mirror.
Draw a ray diagram showing how a concave mirror can be used to produce a real, inverted and diminished image of an object.
Write down a formula for the magnification produced by a concave mirror.
in terms of height of object and height of image
A concave mirror has a focal length of 4 cm and an object 2 cm tall is placed 9 cm away from it. Find the nature, position and size of the image formed.
A large concave mirror has a radius of curvature of 1.5 m. A person stands 10 m in front of the mirror. Where is the person's image?
The mirror used by a dentist to examine the teeth of a person is:
(d) any one of the above
(a) convex
(b) concave
(c) plane
(d) any one of the above
______ is used as reflectors in torchlight.
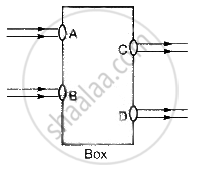
Beams of light are incident through the holes A and B and emerge out of box through the holes C and D respectively as shown in the figure. Which of the following could be inside the box?
Rays from Sun converge at a point 15 cm in front of a concave mirror. Where should an object be placed so that size of its image is equal to the size of the object?
______ mirrors make things look larger when objects are placed close to them.
Which type of mirror is used in the following?
Head lamps of a car
